B-52 Flying Fortress: Iconic Bomber Plane History

Evolution of the B-52 Flying Fortress: A Legendary Bomber Plane

The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, commonly known as the B-52 Flying Fortress, has been a cornerstone of the United States military’s aerial capabilities for over six decades. With its impressive size, range, and payload capacity, this iconic bomber has played a significant role in shaping the course of modern military history. In this article, we’ll delve into the development, design, and operational history of the B-52 Flying Fortress, highlighting its key features, notable missions, and impact on the world.
Conception and Development

In the aftermath of World War II, the United States Air Force (USAF) recognized the need for a strategic bomber capable of delivering nuclear payloads across intercontinental distances. In 1946, Boeing, Convair, and North American Aviation submitted proposals for a new bomber design. Boeing’s proposal, led by designer Ed Wells, ultimately won the contract, and the B-52 program was officially launched.
The B-52’s design was influenced by the earlier B-47 Stratojet and B-29 Superfortress. However, it featured significant innovations, including a high-aspect-ratio wing, eight jet engines, and a reduced radar cross-section. The aircraft’s flying wing design and swept wings provided exceptional stability and lift, making it an ideal platform for long-range missions.
Key Features and Design
The B-52 Flying Fortress boasts an impressive array of features that have contributed to its enduring success:
- Range and Speed: With a maximum range of over 8,800 miles (14,160 km) and a cruising speed of approximately 525 mph (845 km/h), the B-52 can deliver payloads across vast distances.
- Payload Capacity: The B-52 can carry up to 70,000 pounds (31,751 kg) of ordnance, including nuclear and conventional bombs, missiles, and mines.
- Defensive Armament: The aircraft is equipped with four 0.50-inch (12.7 mm) machine guns and a tail turret, providing defensive capabilities against enemy fighters.
- Crew and Cockpit: The B-52 has a crew of five, including a pilot, co-pilot, navigator, bombardier, and gunner. The cockpit features a distinctive bubble canopy, providing exceptional visibility for the crew.
Operational History

The B-52 has played a significant role in various military conflicts and operations:
- Cold War: The B-52 served as a deterrent against Soviet aggression, with many aircraft stationed in Europe and Asia.
- Vietnam War: B-52s conducted bombing missions against North Vietnamese targets, including the infamous Operation Linebacker II.
- Gulf War: B-52s participated in Operation Desert Storm, delivering precision-guided munitions against Iraqi targets.
- War in Afghanistan: B-52s have supported coalition forces, conducting bombing missions against Taliban and al-Qaeda targets.
💡 Note: The B-52 has also played a significant role in various humanitarian and disaster relief operations, including the 2010 Haiti earthquake and the 2013 Typhoon Haiyan relief efforts.
Notable Variants and Upgrades

The B-52 has undergone several upgrades and modifications throughout its service life:
- B-52A: The first production variant, featuring a distinctive “tall tail” design.
- B-52D: Introduced in the late 1950s, this variant featured improved engines and avionics.
- B-52G: The most widely produced variant, featuring a redesigned tail and improved defensive systems.
- B-52H: The final production variant, featuring improved engines and avionics.
Legacy and Impact

The B-52 Flying Fortress has left an indelible mark on modern military history:
- Deterrent: The B-52’s nuclear capabilities have served as a deterrent against potential aggressors.
- Technological Advancements: The B-52 has driven innovation in aviation, with its design influencing later bomber aircraft.
- Iconic Status: The B-52 has become an iconic symbol of American military power, appearing in numerous films, books, and media.
As the B-52 Flying Fortress continues to serve in the United States Air Force, its legacy as a testament to innovation, engineering, and military prowess remains unwavering.
What is the maximum range of the B-52 Flying Fortress?

+
The maximum range of the B-52 Flying Fortress is approximately 8,800 miles (14,160 km).
How many engines does the B-52 have?

+
The B-52 Flying Fortress has eight jet engines.
What is the crew composition of the B-52?
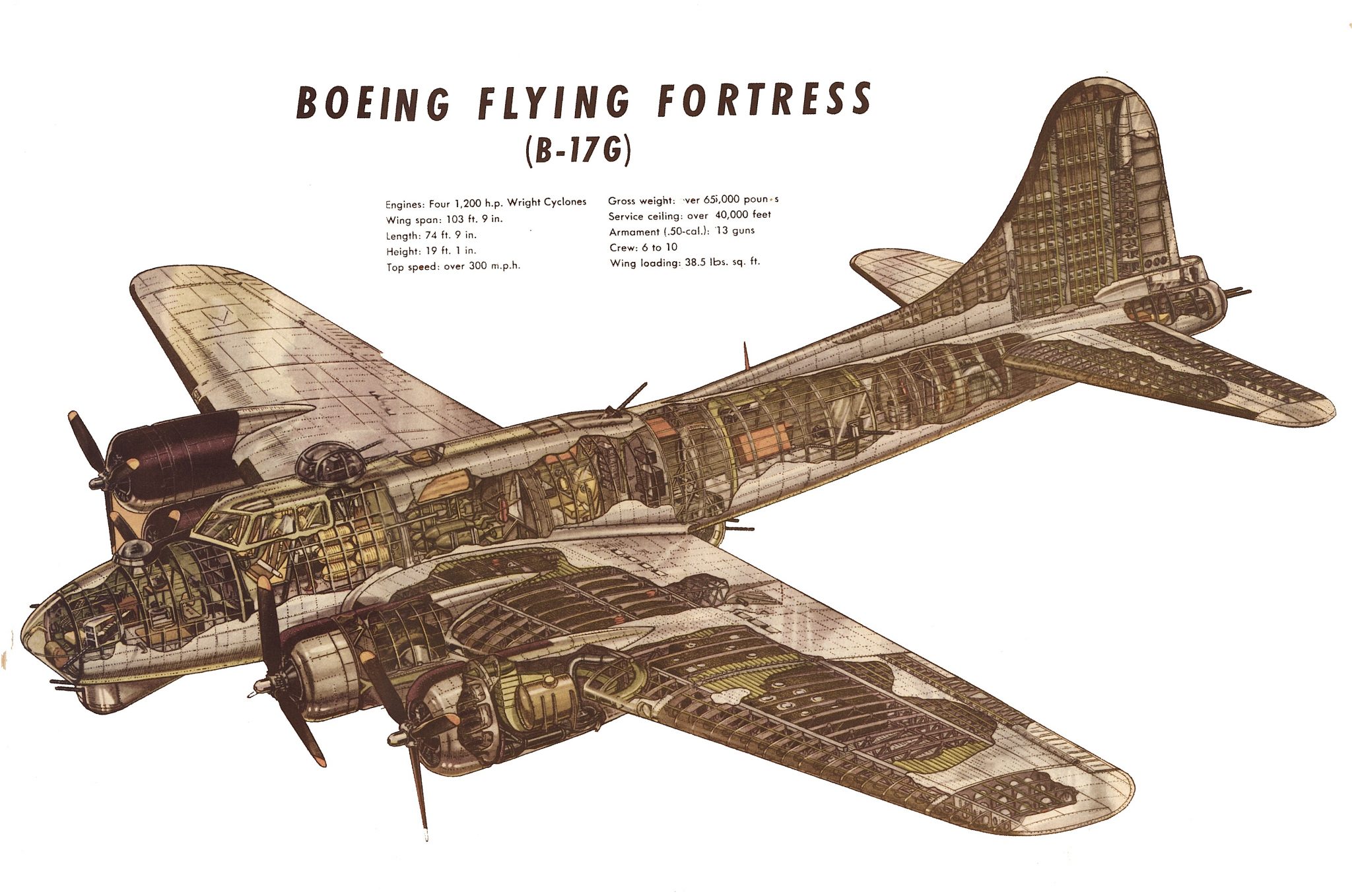
+
The B-52 has a crew of five, including a pilot, co-pilot, navigator, bombardier, and gunner.