Benchmarks Better Than Bogomips

Understanding the Limitations of Bogomips
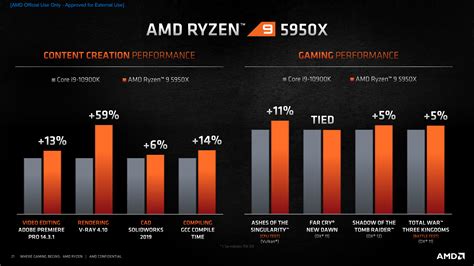
When it comes to measuring CPU performance, one term that has been widely used is “bogomips.” However, as technology advances and CPUs become more complex, the concept of bogomips has become increasingly outdated. In this article, we will explore the limitations of bogomips and discuss better alternatives for measuring CPU performance.
What are Bogomips?

Bogomips is a measure of CPU performance that was originally designed to provide a rough estimate of a CPU’s processing power. The term “bogomips” is a play on the word “mips,” which stands for “million instructions per second.” Bogomips were calculated by running a simple benchmarking program that measured the time it took for a CPU to execute a series of instructions. The result was then used to estimate the CPU’s processing power in terms of millions of instructions per second.
Limitations of Bogomips

While bogomips were useful in the early days of computing, they have several limitations that make them unsuitable for modern CPUs. Some of the key limitations of bogomips include:
- Simplistic measurement: Bogomips are based on a simple benchmarking program that does not accurately reflect real-world workloads.
- Lack of context: Bogomips do not take into account other factors that affect CPU performance, such as memory bandwidth, cache size, and instruction-level parallelism.
- Inconsistent results: Bogomips can produce inconsistent results depending on the specific benchmarking program used and the system configuration.
- Outdated: Bogomips were designed for older CPUs and do not accurately reflect the performance of modern CPUs.
Better Alternatives to Bogomips

So, what are some better alternatives to bogomips for measuring CPU performance? Here are a few options:
- SPEC CPU: The Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation (SPEC) CPU benchmark is a widely used benchmarking program that measures CPU performance using a variety of workloads, including integer and floating-point calculations.
- Geekbench: Geekbench is a popular benchmarking program that measures CPU performance using a variety of workloads, including integer and floating-point calculations, as well as memory bandwidth and cache performance.
- Cinebench: Cinebench is a benchmarking program that measures CPU performance using a variety of workloads, including 3D rendering and video encoding.
Key Features of Better Benchmarks
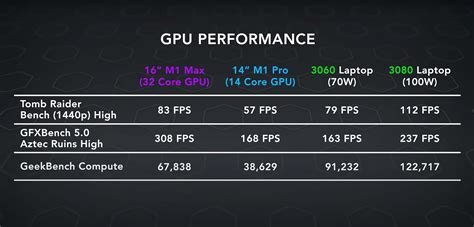
What makes these benchmarks better than bogomips? Here are some key features:
- Multi-threading: Better benchmarks take into account the ability of modern CPUs to execute multiple threads simultaneously.
- Real-world workloads: Better benchmarks use real-world workloads that reflect the types of tasks that users typically perform on their computers.
- Context-aware: Better benchmarks take into account other factors that affect CPU performance, such as memory bandwidth, cache size, and instruction-level parallelism.
Conclusion
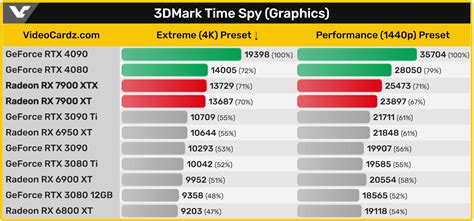
In conclusion, while bogomips were once a useful measure of CPU performance, they have become increasingly outdated. Better alternatives, such as SPEC CPU, Geekbench, and Cinebench, provide a more accurate and comprehensive measure of CPU performance. By using these benchmarks, users can get a better understanding of their CPU’s capabilities and make more informed purchasing decisions.
What is the main limitation of bogomips?
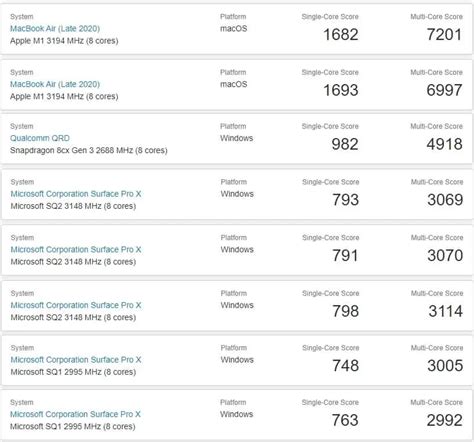
+
The main limitation of bogomips is that they are based on a simplistic measurement that does not accurately reflect real-world workloads.
What is a better alternative to bogomips?

+
Better alternatives to bogomips include SPEC CPU, Geekbench, and Cinebench, which provide a more accurate and comprehensive measure of CPU performance.
Why are multi-threading and real-world workloads important in CPU benchmarks?
+
Multi-threading and real-world workloads are important in CPU benchmarks because they reflect the types of tasks that users typically perform on their computers and provide a more accurate measure of CPU performance.



