Mastering Bloom's Taxonomy: Action Verbs for Deeper Learning
Understanding Bloom's Taxonomy
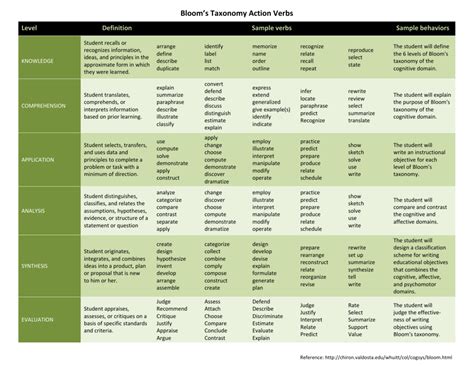
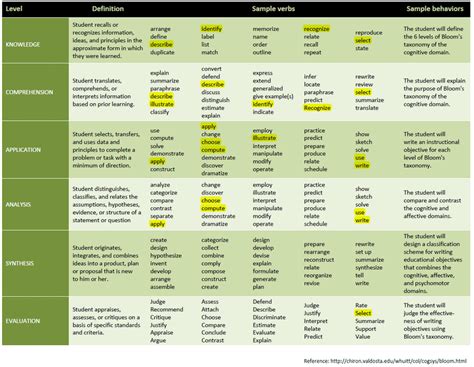
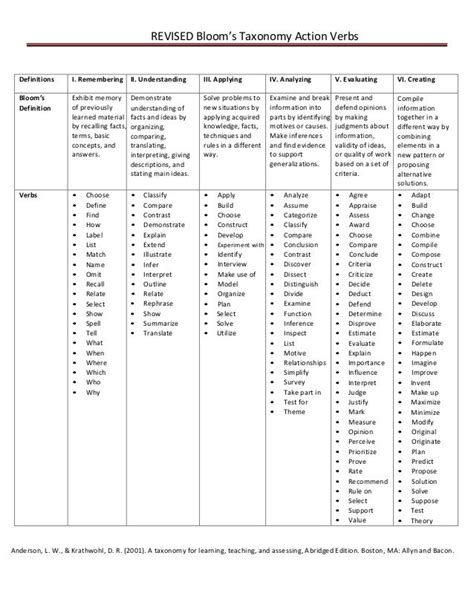
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a widely used framework in education that helps teachers create learning objectives and assessments that promote critical thinking and deeper learning. The taxonomy was first introduced by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues in 1956 and has since undergone several revisions. The framework categorizes learning objectives into six levels of cognitive complexity, ranging from basic recall to complex evaluation and creation.
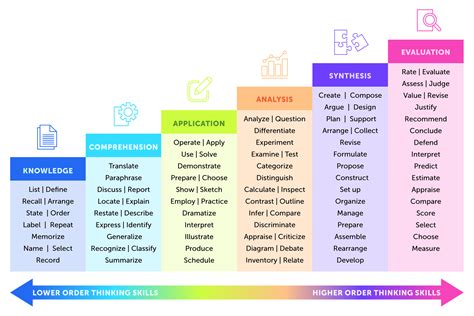
The Six Levels of Bloom's Taxonomy
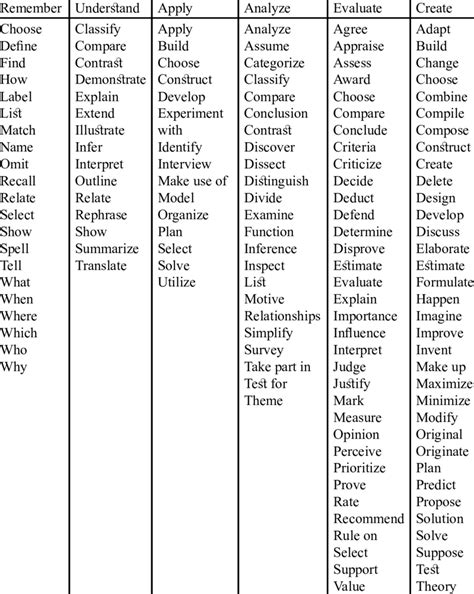
Each level of Bloom’s Taxonomy is associated with specific action verbs that describe the type of thinking required. Here are the six levels, along with examples of action verbs for each:
- Remembering: Recall previously learned information.
- Action verbs: define, describe, identify, label, list, match, name, recall, recognize
- Understanding: Interpret and make sense of information.
- Action verbs: analyze, classify, compare, contrast, describe, explain, illustrate, infer, outline, summarize
- Applying: Use learned information to solve problems or complete tasks.
- Action verbs: apply, calculate, complete, demonstrate, develop, employ, examine, operate, practice, show
- Analyzing: Break down complex information into smaller parts to understand relationships and patterns.
- Action verbs: analyze, categorize, compare, contrast, deduce, diagram, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, evaluate
- Evaluating: Make judgments about the value or quality of information.
- Action verbs: appraise, argue, assess, compare, conclude, criticize, debate, deduce, evaluate, justify
- Creating: Generate new ideas, products, or solutions.
- Action verbs: compose, construct, create, design, develop, formulate, generate, invent, model, plan
Using Action Verbs to Create Learning Objectives

When creating learning objectives, it’s essential to use action verbs that align with the desired level of cognitive complexity. Here are some examples of learning objectives that use action verbs from each level of Bloom’s Taxonomy:
- Remembering: Students will be able to define the key terms related to cell biology.
- Understanding: Students will be able to explain the concept of mitosis and its role in cell reproduction.
- Applying: Students will be able to apply the principles of Newton’s laws to solve problems involving motion.
- Analyzing: Students will be able to analyze a case study to identify the causes and effects of a social issue.
- Evaluating: Students will be able to evaluate the effectiveness of a marketing campaign based on its target audience and message.
- Creating: Students will be able to design a new product or service that addresses a specific need or problem.
📝 Note: Using action verbs from Bloom's Taxonomy helps to ensure that learning objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Assessment Strategies for Each Level

Assessment strategies should align with the level of cognitive complexity required by the learning objective. Here are some examples of assessment strategies for each level:
- Remembering: Multiple-choice questions, true/false questions, fill-in-the-blank questions
- Understanding: Short-answer questions, essay questions, concept maps
- Applying: Problem-solving tasks, case studies, simulations
- Analyzing: Analytic essays, debates, discussions
- Evaluating: Peer review, self-assessment, evaluation rubrics
- Creating: Project-based assessments, presentations, portfolios
Table: Action Verbs and Assessment Strategies
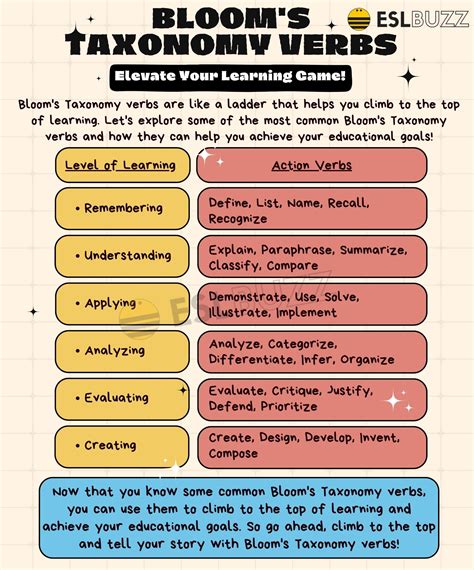
| Level of Bloom's Taxonomy | Action Verbs | Assessment Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Remembering | define, describe, identify, label, list, match, name, recall, recognize | Multiple-choice questions, true/false questions, fill-in-the-blank questions |
| Understanding | analyze, classify, compare, contrast, describe, explain, illustrate, infer, outline, summarize | Short-answer questions, essay questions, concept maps |
| Applying | apply, calculate, complete, demonstrate, develop, employ, examine, operate, practice, show | Problem-solving tasks, case studies, simulations |
| Analyzing | analyze, categorize, compare, contrast, deduce, diagram, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, evaluate | Analytic essays, debates, discussions |
| Evaluating | appraise, argue, assess, compare, conclude, criticize, debate, deduce, evaluate, justify | Peer review, self-assessment, evaluation rubrics |
| Creating | compose, construct, create, design, develop, formulate, generate, invent, model, plan | Project-based assessments, presentations, portfolios |

📝 Note: This table provides a summary of the action verbs and assessment strategies for each level of Bloom's Taxonomy.
Conclusion
Mastering Bloom’s Taxonomy requires a deep understanding of the six levels of cognitive complexity and the action verbs that describe each level. By using action verbs from Bloom’s Taxonomy, educators can create learning objectives that promote critical thinking and deeper learning. Additionally, assessment strategies should align with the level of cognitive complexity required by the learning objective. By using this framework, educators can create a more comprehensive and effective learning environment.
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
+
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework that categorizes learning objectives into six levels of cognitive complexity, ranging from basic recall to complex evaluation and creation.
What are the six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy?
+
The six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy are Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating.
How do I use action verbs from Bloom’s Taxonomy to create learning objectives?

+
Use action verbs from Bloom’s Taxonomy to create specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) learning objectives. For example, “Students will be able to define the key terms related to cell biology.”



