7 Buildings with Buffer Zones for Enhanced Safety
Designing for Disaster: 7 Buildings with Buffer Zones for Enhanced Safety
In the face of natural disasters and security threats, architects and engineers are turning to innovative design solutions to protect buildings and their occupants. One such strategy is the incorporation of buffer zones, which serve as a protective barrier between the building and potential hazards. Here, we explore 7 buildings that have implemented buffer zones to enhance safety and mitigate risks.
1. The Guggenheim Museum, Bilbao, Spain

The Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain, features a unique buffer zone design. The building’s atrium is surrounded by a series of curved glass walls that provide a secure buffer zone between the museum and the surrounding city. This design not only provides a sense of openness and transparency but also serves as a protective barrier against potential security threats.
2. The Willis Tower (formerly Sears Tower), Chicago, USA

The Willis Tower, one of the tallest buildings in the world, features a buffer zone design to protect against extreme weather conditions. The building’s foundation is surrounded by a series of deep foundations and a concrete slab that provides a secure buffer zone against strong winds and seismic activity.
3. The Taipei 101, Taipei, Taiwan

The Taipei 101 skyscraper features a unique damper system that serves as a buffer zone against seismic activity. The system, known as a steel pendulum damper, is designed to absorb and dissipate the energy generated by seismic waves, reducing the stress on the building’s structure.
4. The Reichstag Building, Berlin, Germany

The Reichstag Building in Berlin features a buffer zone design to protect against security threats. The building’s facade is surrounded by a series of bollards and a reinforced glass wall that provides a secure barrier against potential attacks.
5. The CN Tower, Toronto, Canada
The CN Tower features a buffer zone design to protect against extreme weather conditions. The tower’s foundation is surrounded by a series of deep foundations and a concrete slab that provides a secure buffer zone against strong winds and ice storms.
6. The Petronas Twin Towers, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
The Petronas Twin Towers feature a unique buffer zone design to protect against seismic activity. The towers’ foundations are surrounded by a series of deep foundations and a concrete slab that provides a secure buffer zone against seismic waves.
7. The Burj Khalifa, Dubai, UAE
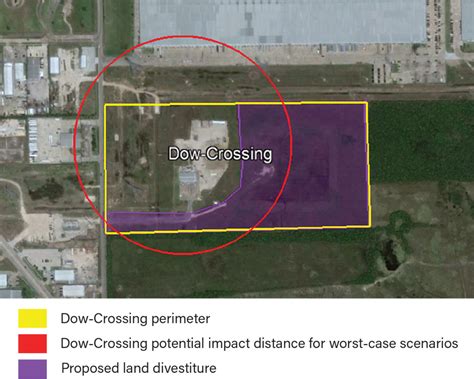
The Burj Khalifa, the tallest building in the world, features a buffer zone design to protect against extreme weather conditions. The building’s foundation is surrounded by a series of deep foundations and a concrete slab that provides a secure buffer zone against strong winds and seismic activity.
🌪️ Note: Buffer zones can be designed to protect against a wide range of hazards, including natural disasters, security threats, and extreme weather conditions.
In conclusion, the incorporation of buffer zones in building design can provide an effective means of enhancing safety and mitigating risks. By understanding the potential hazards and designing buildings with buffer zones, architects and engineers can create safer and more resilient structures that protect occupants and assets.
What is a buffer zone in building design?

+
A buffer zone is a protective barrier or area designed to absorb or dissipate the energy generated by potential hazards, such as natural disasters, security threats, or extreme weather conditions.
What are the benefits of incorporating buffer zones in building design?
+
The benefits of incorporating buffer zones in building design include enhanced safety, reduced risk, and improved resilience against potential hazards.
Can buffer zones be designed to protect against multiple hazards?
+
Yes, buffer zones can be designed to protect against multiple hazards, including natural disasters, security threats, and extreme weather conditions.


