Transfer Between Military Branches Made Easy

Understanding the Process of Transferring Between Military Branches
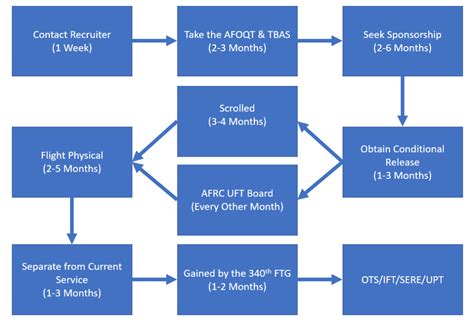
For various reasons, some military personnel may consider transferring from one branch of the military to another. This could be due to a desire for a change of pace, a new challenge, or to align with their career goals. Whatever the reason, transferring between military branches can be a complex process. In this article, we will break down the steps involved in transferring between military branches, highlighting the requirements, benefits, and potential challenges.
Why Transfer Between Military Branches?

There are several reasons why a military personnel may want to transfer between branches. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Career Advancement: Transferring to a different branch may provide better opportunities for career advancement, especially if the current branch has limited promotion opportunities.
- Change of Pace: A transfer can provide a change of pace and a new challenge, which can be beneficial for personal and professional growth.
- Family Reasons: In some cases, a transfer may be necessary due to family reasons, such as a spouse’s job relocation or family health issues.
- Education and Training: Transferring to a different branch may provide access to specialized education and training, which can enhance career prospects.
Eligibility Requirements for Transferring Between Military Branches

To be eligible to transfer between military branches, personnel must meet certain requirements. These include:
- Current Enlistment: The personnel must be currently enlisted in one of the military branches.
- Good Standing: The personnel must be in good standing, with no pending disciplinary actions or unresolved medical issues.
- Qualifying Score: The personnel must meet the qualifying score for the branch they wish to transfer to.
- Time in Service: The personnel must have completed their initial service obligation, typically 4-6 years.
Steps to Transfer Between Military Branches

The process of transferring between military branches involves several steps:
- Meet with a Career Counselor: The personnel must meet with a career counselor to discuss their reasons for transferring and to determine if they meet the eligibility requirements.
- Complete the Application: The personnel must complete the application for inter-service transfer, which includes providing personal and professional information.
- Take the Qualifying Exam: The personnel must take the qualifying exam for the branch they wish to transfer to.
- Medical Screening: The personnel must undergo a medical screening to ensure they meet the medical standards for the new branch.
- Background Check: The personnel must undergo a background check to ensure they meet the security clearance requirements for the new branch.
- Interview with a Recruiter: The personnel must interview with a recruiter from the new branch to discuss their application and qualifications.
- Receive Approval: The personnel must receive approval from the current branch and the new branch before the transfer can be processed.
🚨 Note: The transfer process can take several months to complete, and personnel must be prepared to wait for the approval process to be completed.
Benefits of Transferring Between Military Branches

Transferring between military branches can provide several benefits, including:
- New Challenges: A transfer can provide new challenges and opportunities for personal and professional growth.
- Career Advancement: Transferring to a different branch may provide better opportunities for career advancement.
- Increased Pay: In some cases, transferring to a different branch may result in increased pay and benefits.
- Broader Skill Set: Transferring to a different branch can provide the opportunity to develop a broader skill set and gain new experiences.
Challenges of Transferring Between Military Branches

While transferring between military branches can be beneficial, it also comes with some challenges, including:
- Uncertainty: The transfer process can be uncertain, and personnel may face delays or rejection.
- Loss of Seniority: Transferring to a different branch may result in a loss of seniority and rank.
- Adjustment Period: Transferring to a different branch can require an adjustment period, as personnel adapt to new policies, procedures, and cultures.
Conclusion

Transferring between military branches can be a complex process, but it can also provide new challenges, opportunities for career advancement, and a broader skill set. By understanding the eligibility requirements, steps involved in the transfer process, and the benefits and challenges of transferring, military personnel can make informed decisions about their career.
What is the typical processing time for an inter-service transfer?

+
The typical processing time for an inter-service transfer can take several months to complete, typically 3-6 months.
Can I transfer to a different branch if I have a medical condition?

+
Yes, but you must meet the medical standards for the new branch. You may need to undergo a medical screening to determine your eligibility.
Will I lose my rank if I transfer to a different branch?

+
Yes, you may lose your rank if you transfer to a different branch. Your rank will be determined by the new branch based on your qualifications and experience.
Related Terms:
- Inter service transfer



