7 Concussion Movie Medical Facts Revealed

Understanding Concussions: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Movie Concussion

The movie Concussion, released in 2015, tells the story of Dr. Bennet Omalu, a forensic pathologist who discovers the link between head trauma and brain damage in American football players. The film highlights the controversy surrounding the National Football League’s (NFL) handling of player concussions and the devastating effects of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) on players’ lives. While the movie takes creative liberties with the true events, it also sheds light on some important medical facts about concussions and their long-term consequences.
1. Concussions are a Type of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)

A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a blow to the head or body that can cause the brain to move back and forth inside the skull. This movement can lead to chemical changes in the brain and damage to brain cells.
🧠 Note: Concussions can occur even if there is no visible injury to the head.
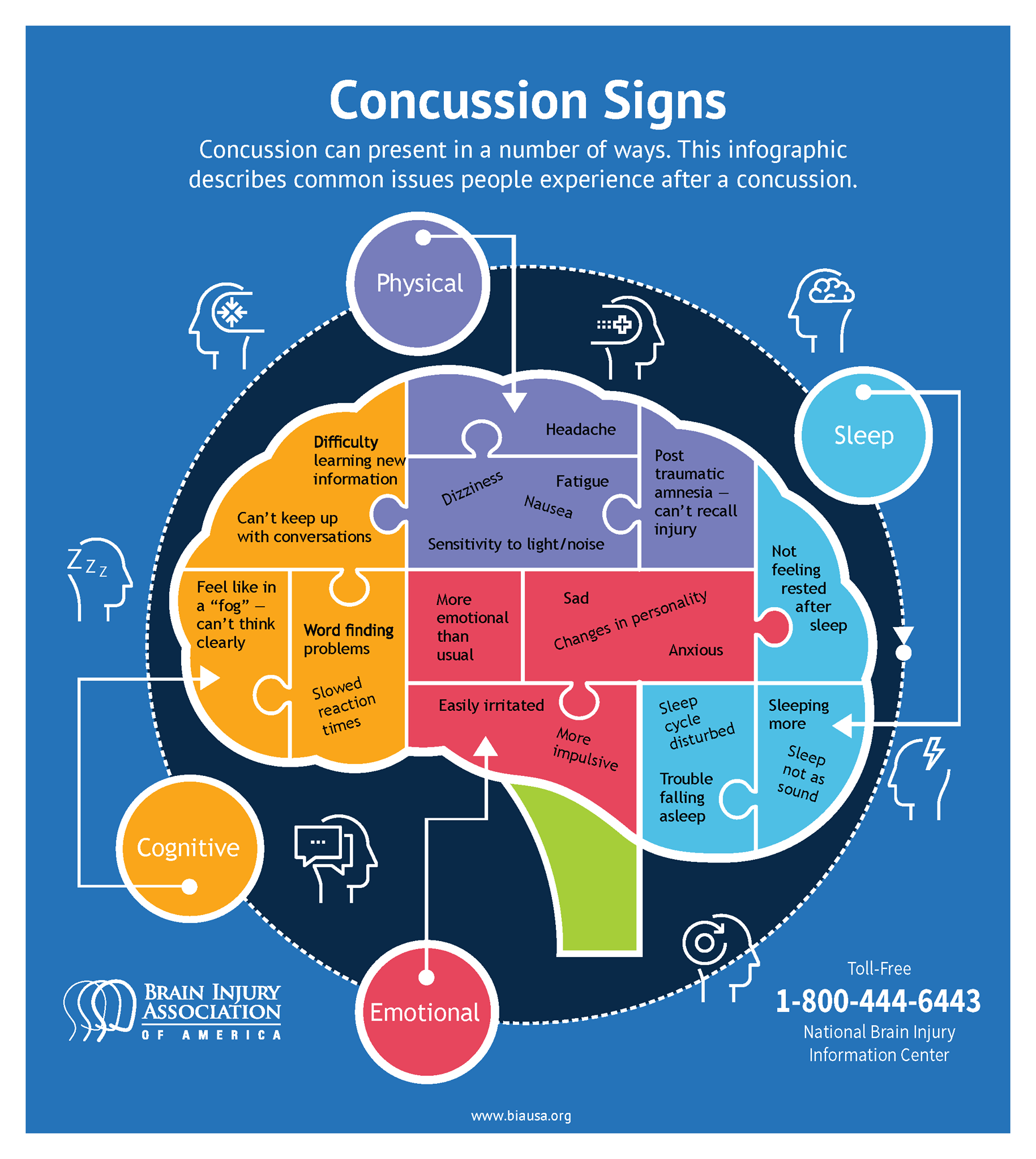
2. Symptoms of a Concussion Can be Subtle

Concussion symptoms can be difficult to recognize, especially in the days and weeks following the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Confusion and disorientation
- Memory loss and difficulty concentrating
- Mood changes, such as irritability and anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Sensitivity to light and noise
- Headaches and dizziness
🤕 Note: Some people may not exhibit any symptoms at all, or they may not appear until days or weeks after the injury.
3. Repetitive Head Trauma Increases the Risk of CTE

Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a degenerative brain disease caused by repetitive head trauma, such as that experienced by football players. CTE can lead to memory loss, depression, anxiety, and dementia, among other symptoms.
| Stage of CTE | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Mood changes, depression, and anxiety |
| Stage 2 | Short-term memory loss and difficulty concentrating |
| Stage 3 | Cognitive decline, including difficulty with speech and language |
| Stage 4 | Severe dementia, including loss of motor function and difficulty with daily activities |
4. CTE Can Only be Diagnosed After Death

Currently, CTE can only be diagnosed after death, through an autopsy and examination of brain tissue. Researchers are working to develop tests to diagnose CTE in living individuals, but these tests are still in the experimental stages.
5. Helmets and Safety Equipment are Not Enough to Prevent Concussions

While helmets and safety equipment can help reduce the risk of head injury, they are not enough to prevent concussions. Concussions can occur even with proper safety equipment, and the risk of injury is still present even with the latest technology.
💡 Note: Reducing the number of head impacts, rather than just relying on safety equipment, is key to preventing concussions.
6. Rest and Recovery are Critical After a Concussion

After a concussion, rest and recovery are critical to allowing the brain to heal. This includes avoiding physical activity, getting plenty of sleep, and avoiding stimulating activities.
🛋️ Note: Ignoring concussion symptoms or returning to play too quickly can lead to further injury and long-term consequences.
7. There is No Cure for CTE, But Researchers are Working to Find Treatments

Currently, there is no cure for CTE, but researchers are working to develop treatments to manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
While the movie Concussion takes some creative liberties with the true events, it shines a light on the important medical facts surrounding concussions and CTE. By understanding these facts, we can work to reduce the risk of head injury and promote better brain health for athletes and individuals of all ages.
The findings of Dr. Bennet Omalu and other researchers have led to changes in the way the NFL approaches head injuries and concussions. While there is still much to be learned, the progress made so far is a step in the right direction towards prioritizing player safety and promoting better brain health.
What is a concussion?

+
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a blow to the head or body that can cause the brain to move back and forth inside the skull.
Can concussions be prevented?

+
While helmets and safety equipment can help reduce the risk of head injury, they are not enough to prevent concussions. Reducing the number of head impacts is key to preventing concussions.
What is CTE?

+
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a degenerative brain disease caused by repetitive head trauma, such as that experienced by football players.