5 Key Differences: Cyanocobalamin vs Methylcobalamin

Understanding the Differences: Cyanocobalamin vs Methylcobalamin
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in various bodily functions, including the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. There are several forms of vitamin B12, but two of the most commonly discussed are cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin. While both forms can be used to treat vitamin B12 deficiencies, they have distinct differences in terms of their structure, absorption, and effects on the body.
1. Chemical Structure

Cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin differ in their chemical structure. Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic form of vitamin B12 that contains a cyanide molecule. This form is commonly used in vitamin supplements and fortified foods due to its stability and low cost. On the other hand, methylcobalamin is a naturally occurring form of vitamin B12 that contains a methyl group. This form is found in animal products and is considered more bioavailable than cyanocobalamin.
2. Absorption and Utilization
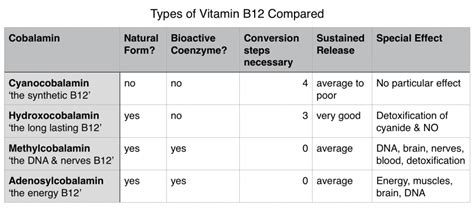
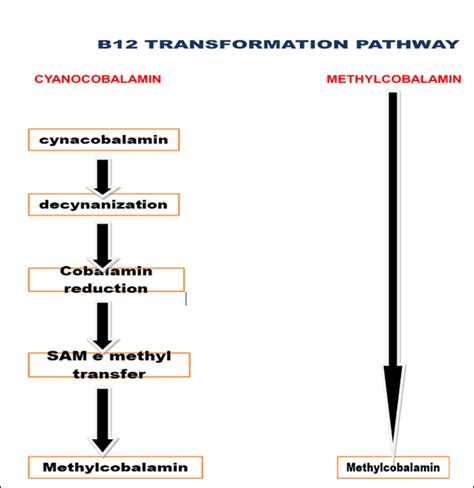
The absorption and utilization of cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin differ significantly. Cyanocobalamin is not easily absorbed by the body and requires conversion to other forms of vitamin B12, such as methylcobalamin, to be utilized. This conversion process occurs in the liver and requires the presence of specific enzymes. Methylcobalamin, on the other hand, is more easily absorbed and can be used directly by the body.
Key differences in absorption:
- Cyanocobalamin: Requires conversion to other forms, such as methylcobalamin, to be utilized.
- Methylcobalamin: Can be used directly by the body.
3. Effectiveness in Treating Deficiencies

Both cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin can be used to treat vitamin B12 deficiencies, but methylcobalamin is considered more effective. Studies have shown that methylcobalamin is better absorbed and retained in the body than cyanocobalamin, leading to faster and more effective treatment of deficiencies.
Comparison of effectiveness:
- Cyanocobalamin: May require higher doses and longer treatment periods to achieve desired results.
- Methylcobalamin: Can produce faster and more effective results due to its higher bioavailability.
4. Side Effects and Interactions

Cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin have different side effect profiles and interaction risks. Cyanocobalamin can cause skin rashes, itching, and hives in some individuals, while methylcobalamin is generally considered safe and well-tolerated.
Comparison of side effects:
- Cyanocobalamin: May cause skin rashes, itching, and hives in some individuals.
- Methylcobalamin: Generally considered safe and well-tolerated.
5. Cost and Availability
Cyanocobalamin is generally less expensive than methylcobalamin, which can make it a more appealing option for some individuals. However, the cost difference may not be significant enough to outweigh the benefits of using methylcobalamin.
Comparison of cost:
- Cyanocobalamin: Generally less expensive than methylcobalamin.
- Methylcobalamin: May be more expensive than cyanocobalamin, but offers better bioavailability and effectiveness.
👉 Note: The cost difference between cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin may vary depending on the manufacturer, quality, and source of the supplement.
In conclusion, while both cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin can be used to treat vitamin B12 deficiencies, they have distinct differences in terms of their structure, absorption, and effects on the body. Methylcobalamin is generally considered more effective and better tolerated than cyanocobalamin, making it a popular choice among healthcare professionals and individuals looking for a high-quality vitamin B12 supplement.
What is the main difference between cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin?

+
The main difference between cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin is their chemical structure and bioavailability. Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic form of vitamin B12 that contains a cyanide molecule, while methylcobalamin is a naturally occurring form that contains a methyl group.
Which form of vitamin B12 is more effective in treating deficiencies?
+
Methylcobalamin is generally considered more effective in treating vitamin B12 deficiencies due to its higher bioavailability and ability to be used directly by the body.
Are there any side effects associated with cyanocobalamin?

+
Yes, cyanocobalamin can cause skin rashes, itching, and hives in some individuals. Methylcobalamin is generally considered safe and well-tolerated.