US Air Force Reserve: Serve Part-Time, Full-Time Impact
Introduction to the US Air Force Reserve

The United States Air Force Reserve (AFR) is a dynamic and vital part of the nation’s defense strategy, providing part-time service opportunities for individuals to contribute to the country’s military readiness. By serving part-time, Airmen in the Air Force Reserve can have a full-time impact on national security while also maintaining their civilian careers and lifestyles.
History and Mission of the US Air Force Reserve

The Air Force Reserve was established on April 14, 1948, as a separate component of the US Air Force. Since its inception, the AFR has played a critical role in supplementing the active-duty Air Force during times of war and national crisis. The mission of the Air Force Reserve is to provide combat-ready units and individuals to support the nation’s defense strategy, while also serving as a strategic reserve force to augment the active-duty Air Force.
Benefits of Serving in the US Air Force Reserve

Serving in the Air Force Reserve offers a wide range of benefits, including:
- Part-time service: Airmen typically serve one weekend a month (known as a Unit Training Assembly, or UTA) and two weeks a year (known as Annual Tour, or AT).
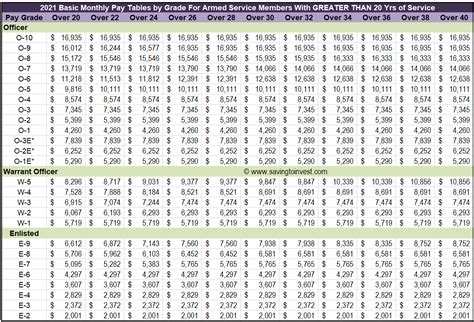
- Competitive pay and benefits: Airmen receive pay and benefits comparable to those in the active-duty Air Force, including access to base facilities, shopping privileges, and travel opportunities.
- Education assistance: The Air Force Reserve offers tuition assistance and education benefits to help Airmen pursue higher education.
- Career advancement: Serving in the Air Force Reserve can enhance civilian career prospects and provide opportunities for professional development.
- Camaraderie and esprit de corps: Airmen in the Air Force Reserve develop lasting bonds with fellow Airmen and experience the pride and satisfaction of serving their country.
How to Join the US Air Force Reserve

To join the Air Force Reserve, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements, including:
- Age: Be between the ages of 17 and 39 (with some exceptions for older candidates).
- Citizenship: Be a US citizen.
- Education: Have a high school diploma or equivalent.
- Physical fitness: Meet Air Force physical fitness standards.
- Background check: Pass a background check.
The enlistment process typically involves the following steps:
- Meet with a recruiter: Discuss career goals and determine if the Air Force Reserve is the right fit.
- Take the ASVAB test: Assess aptitude for various career fields.
- Choose a career field: Select from over 100 Air Force Reserve career fields, including medical, administrative, and technical specialties.
- Attend Basic Military Training (BMT): Complete seven weeks of training at Lackland Air Force Base, Texas.
- Attend technical training: Receive specialized training in the chosen career field.
💡 Note: The enlistment process may vary depending on individual circumstances, such as prior military service or college credits.
Career Fields in the US Air Force Reserve

The Air Force Reserve offers a wide range of career fields, including:
- Medical careers: Nursing, medicine, dentistry, and pharmacy.
- Administrative careers: Human resources, finance, and administration.
- Technical careers: Maintenance, logistics, and communications.
- Cybersecurity careers: Network operations, cybersecurity, and intelligence.
Some of the most in-demand career fields in the Air Force Reserve include:
- Cybersecurity specialists: Protect Air Force networks and systems from cyber threats.
- Intelligence analysts: Analyze and interpret intelligence data to support national security decisions.
- Logistics specialists: Manage the movement of personnel, equipment, and supplies.
- Maintenance specialists: Repair and maintain aircraft, vehicles, and equipment.
Conclusion

Serving in the US Air Force Reserve offers a unique opportunity to make a full-time impact on national security while serving part-time. With a wide range of career fields, competitive pay and benefits, and opportunities for education and career advancement, the Air Force Reserve is an attractive option for individuals who want to serve their country while maintaining their civilian lives.
What is the difference between the Air Force Reserve and the active-duty Air Force?

+
The main difference between the Air Force Reserve and the active-duty Air Force is the level of commitment. Airmen in the Air Force Reserve serve part-time, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year, while active-duty Airmen serve full-time.
Can I serve in the Air Force Reserve if I have prior military service?

+
Yes, individuals with prior military service may be eligible to join the Air Force Reserve. The enlistment process may vary depending on individual circumstances, such as the type of discharge and the amount of time served.
What are the education benefits of serving in the Air Force Reserve?

+
The Air Force Reserve offers tuition assistance and education benefits to help Airmen pursue higher education. These benefits may include the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Air Force Reserve Tuition Assistance Program.
Related Terms:
- Air Force reserves benefits
- Air Force Reserves Pay Chart
- Air Force Reserve pay
- Air Force Reserve Officer
- Air Force Reserve requirements
- Air Force Reserves age limit