Unlocking Endothermic Wavelength: The Science Revealed
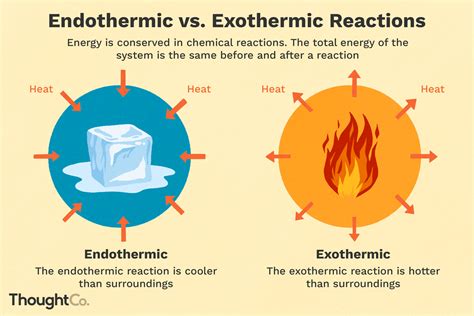
Understanding Endothermic Reactions
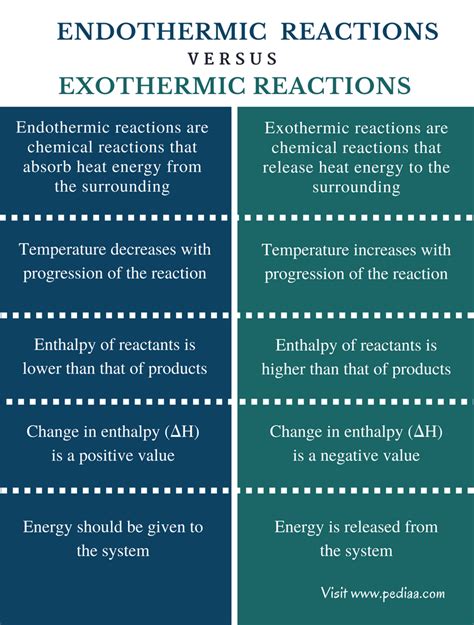
Endothermic reactions are a fundamental concept in chemistry, where a reaction absorbs energy from the surroundings in the form of heat. This energy is then used to break chemical bonds and form new ones, resulting in a more stable product. The energy absorbed during an endothermic reaction is typically in the form of light or heat, and it is this energy that drives the reaction forward.
The Role of Wavelength in Endothermic Reactions
Wavelength plays a crucial role in endothermic reactions, as it determines the amount of energy that is absorbed by the reactants. Different wavelengths of light have different energies, and only certain wavelengths can initiate an endothermic reaction. The wavelength of light that is absorbed by a substance is determined by its molecular structure, and it is this specific wavelength that is responsible for triggering the endothermic reaction.
Unlocking Endothermic Wavelength

Unlocking the endothermic wavelength of a substance requires a deep understanding of its molecular structure and the specific wavelengths of light that it absorbs. This can be achieved through various spectroscopic techniques, such as infrared (IR) spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy. These techniques involve measuring the absorption of light by a substance at different wavelengths, which provides valuable information about its molecular structure and the wavelengths that trigger endothermic reactions.
Applications of Endothermic Wavelength

The applications of endothermic wavelength are diverse and widespread. Some of the most significant applications include:
- Photovoltaic Cells: Endothermic wavelength is used in photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electrical energy. The silicon material in photovoltaic cells absorbs light at specific wavelengths, triggering an endothermic reaction that generates electricity.
- Laser Technology: Endothermic wavelength is used in laser technology to create high-energy beams of light. The specific wavelength of light absorbed by the laser material determines the energy of the beam.
- Medical Applications: Endothermic wavelength is used in medical applications, such as cancer treatment and skin rejuvenation. Specific wavelengths of light are used to target and destroy cancer cells or to stimulate collagen production in the skin.
💡 Note: The specific wavelength of light absorbed by a substance is highly dependent on its molecular structure. Therefore, understanding the molecular structure of a substance is crucial for unlocking its endothermic wavelength.
Challenges and Limitations
Unlocking endothermic wavelength is not without its challenges and limitations. Some of the most significant challenges include:
- Complex Molecular Structures: Understanding the molecular structure of a substance can be challenging, especially for complex molecules. This can make it difficult to identify the specific wavelengths of light that trigger endothermic reactions.
- Interference from Other Reactions: Endothermic reactions can be influenced by other reactions that occur simultaneously, making it difficult to isolate the specific wavelengths of light that trigger the desired reaction.
Future Directions

Despite the challenges and limitations, research into endothermic wavelength continues to advance. Some of the most promising areas of research include:
- Development of New Spectroscopic Techniques: New spectroscopic techniques, such as terahertz spectroscopy, are being developed to study the molecular structure of substances and unlock their endothermic wavelength.
- Application in Emerging Technologies: Endothermic wavelength is being explored for use in emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and optoelectronics.
What is endothermic wavelength?
+
Endothermic wavelength refers to the specific wavelengths of light that are absorbed by a substance to trigger an endothermic reaction.
How is endothermic wavelength measured?

+
Endothermic wavelength can be measured using various spectroscopic techniques, such as infrared (IR) spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy.
What are some applications of endothermic wavelength?
+
Endothermic wavelength has diverse applications, including photovoltaic cells, laser technology, and medical applications.
In conclusion, unlocking endothermic wavelength requires a deep understanding of the molecular structure of a substance and the specific wavelengths of light that trigger endothermic reactions. While there are challenges and limitations to overcome, the applications of endothermic wavelength are diverse and widespread, and research continues to advance in this field.



