Ethnic Group vs Nationality: What's the Difference?

Understanding the Distinction Between Ethnic Group and Nationality

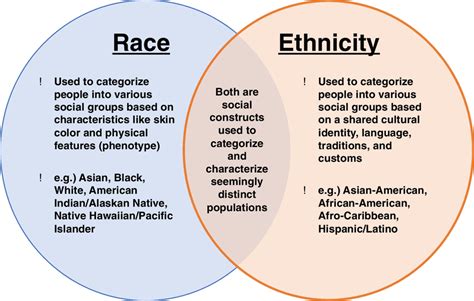
The terms “ethnic group” and “nationality” are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is essential in today’s globalized world, where people from diverse backgrounds interact and coexist. In this article, we will explore the definitions, characteristics, and implications of ethnic group and nationality, highlighting their differences and similarities.
Defining Ethnic Group

An ethnic group refers to a social group that shares a common cultural, linguistic, or ancestral heritage. Members of an ethnic group often identify with a shared history, customs, traditions, and values that distinguish them from other groups. Ethnic groups can be based on various factors, including:
- Language: A shared language or dialect can be a defining characteristic of an ethnic group.
- Culture: Shared customs, traditions, and practices can unite people into an ethnic group.
- Ancestry: A common ancestry or descent can be a basis for ethnic identity.
- Religion: A shared religion or spiritual practice can be a factor in defining an ethnic group.
Examples of ethnic groups include:
- Han Chinese: The largest ethnic group in China, sharing a common language, culture, and ancestry.
- Kurds: An ethnic group spread across several countries in the Middle East, sharing a common language, culture, and history.
- African Americans: An ethnic group in the United States, sharing a common history, culture, and ancestry.
Defining Nationality

Nationality refers to the status of belonging to a particular nation or country. It is often associated with citizenship, which grants individuals rights and responsibilities within a nation-state. Nationality can be based on various factors, including:
- Citizenship: Membership in a nation-state, often acquired through birth, naturalization, or descent.
- Territorial: Residence within a nation-state’s borders.
- Government recognition: Official recognition by a nation-state of an individual’s nationality.
Examples of nationality include:
- American: A person who holds citizenship or is a resident of the United States.
- British: A person who holds citizenship or is a resident of the United Kingdom.
- Indian: A person who holds citizenship or is a resident of India.
Key Differences Between Ethnic Group and Nationality

While there is some overlap between ethnic group and nationality, the key differences lie in their scope and implications:
- Scope: Ethnic group refers to a social group sharing common cultural, linguistic, or ancestral characteristics, whereas nationality refers to membership in a nation-state.
- Implications: Ethnic group identity can influence cultural practices, social interactions, and community affiliations, whereas nationality determines citizenship, rights, and responsibilities within a nation-state.
| Characteristics | Ethnic Group | Nationality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social group sharing common cultural, linguistic, or ancestral heritage | Status of belonging to a particular nation or country |
| Scope | Global or regional | Nation-state or country |
| Implications | Cultural practices, social interactions, community affiliations | Citizenship, rights, responsibilities within a nation-state |
📝 Note: The distinction between ethnic group and nationality is not always clear-cut, as some countries recognize ethnic groups as nationalities, and some ethnic groups may not have a corresponding nationality.
Intersections and Overlaps

While ethnic group and nationality are distinct concepts, they can intersect and overlap in various ways:
- Ethnic nationalism: A form of nationalism that emphasizes the shared identity and interests of a particular ethnic group.
- Multi-ethnic nations: Nations that comprise multiple ethnic groups, such as the United States or India.
- Transnational identities: Identities that transcend national borders, such as the Kurdish identity or the African diaspora.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding the distinction between ethnic group and nationality is crucial in today’s globalized world. By recognizing the differences and similarities between these concepts, we can better appreciate the complexities of identity, culture, and citizenship. As we navigate the complexities of diversity and inclusion, it is essential to approach these concepts with nuance and sensitivity.
What is the difference between ethnic group and nationality?

+
Ethnic group refers to a social group sharing common cultural, linguistic, or ancestral heritage, whereas nationality refers to membership in a nation-state.
Can an individual belong to multiple ethnic groups?

+
Yes, individuals can identify with multiple ethnic groups, and many people have complex or mixed ethnic identities.
Is nationality the same as citizenship?

+
No, nationality and citizenship are related but distinct concepts. Nationality refers to membership in a nation-state, whereas citizenship is a specific status granted by a nation-state to its members.