7 Key Roles of Forensic Anthropology in Investigations

Unraveling the Mysteries of Human Remains: The Vital Role of Forensic Anthropology
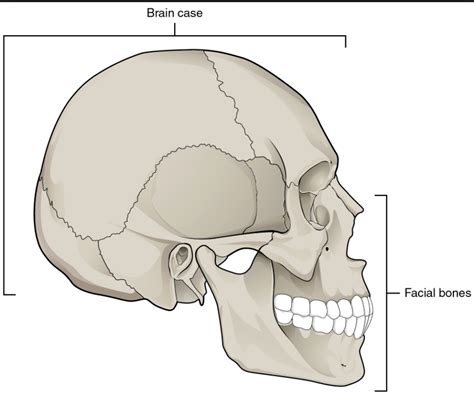
Forensic anthropology is a specialized field that applies the principles of anthropology to aid in the investigation of crimes, particularly those involving human remains. This fascinating discipline has become an essential tool for law enforcement agencies, medical examiners, and coroners in their quest for truth and justice. In this blog post, we will delve into the 7 key roles of forensic anthropology in investigations, highlighting its significance in solving complex cases.
Role 1: Identification of Human Remains

Forensic anthropologists play a crucial role in identifying human remains, which is often a daunting task, especially when the remains are skeletal or severely decomposed. By analyzing the skeletal structure, age, sex, ancestry, and stature, forensic anthropologists can provide valuable information to investigators. This expertise helps to narrow down the search for missing persons and brings closure to families of the deceased.
🔍 Note: Forensic anthropologists use various methods, including radiocarbon dating and stable isotope analysis, to determine the age and origin of human remains.
Role 2: Analysis of Trauma and Cause of Death
Forensic anthropologists examine human remains to determine the cause and manner of death. By analyzing skeletal trauma, such as fractures, cuts, or bullet wounds, they can reconstruct the events surrounding the death. This information is vital in criminal investigations, as it helps to establish the circumstances of the death and identify potential suspects.
Role 3: Estimation of Time Since Death

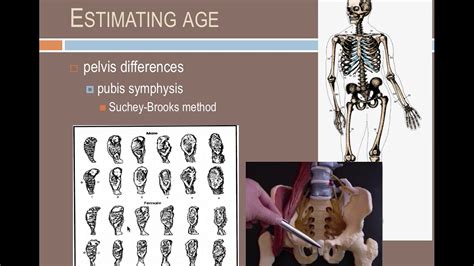
Forensic anthropologists use various methods to estimate the time since death, which is essential in reconstructing the timeline of events surrounding a crime. By analyzing the decomposition rate, insect activity, and other environmental factors, they can provide a relatively accurate estimate of the post-mortem interval (PMI).
Role 4: Reconstruction of the Biological Profile

Forensic anthropologists create a biological profile of the deceased, including their age, sex, ancestry, stature, and weight. This information is useful in identifying unknown individuals and linking them to missing persons cases.
Role 5: Examination of Human Remains for Evidence of Foul Play

Forensic anthropologists inspect human remains for signs of foul play, such as evidence of torture, abuse, or neglect. This examination helps investigators to determine if a crime has been committed and identify potential suspects.
Role 6: Testimony in Court
Forensic anthropologists often testify in court as expert witnesses, providing crucial information to help jurors understand complex evidence. Their testimony can make or break a case, as it provides an objective, scientific perspective on the evidence.
Role 7: Collaboration with Other Experts

Forensic anthropologists work closely with other experts, including forensic pathologists, odontologists, and DNA analysts, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the evidence. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the case are thoroughly examined and that investigators have a complete picture of the events surrounding the crime.
In conclusion, forensic anthropology plays a vital role in investigations, providing crucial information that helps investigators solve complex cases. By applying their expertise in the identification of human remains, analysis of trauma and cause of death, estimation of time since death, reconstruction of the biological profile, examination of human remains for evidence of foul play, testimony in court, and collaboration with other experts, forensic anthropologists contribute significantly to the pursuit of truth and justice.
What is the difference between a forensic anthropologist and a forensic pathologist?

+
A forensic anthropologist specializes in the analysis of human remains, while a forensic pathologist focuses on the examination of soft tissue and the determination of cause and manner of death.
How do forensic anthropologists reconstruct the biological profile of an individual?

+
Forensic anthropologists use various methods, including skeletal analysis, dental examination, and DNA analysis, to reconstruct the biological profile of an individual.
What is the significance of estimating the time since death in forensic anthropology?

+
Estimating the time since death helps investigators to reconstruct the timeline of events surrounding a crime and provides valuable information in missing persons cases.


