7 Ways to Apply Functional Genomic Analysis

Unlocking the Secrets of Genomes: 7 Ways to Apply Functional Genomic Analysis
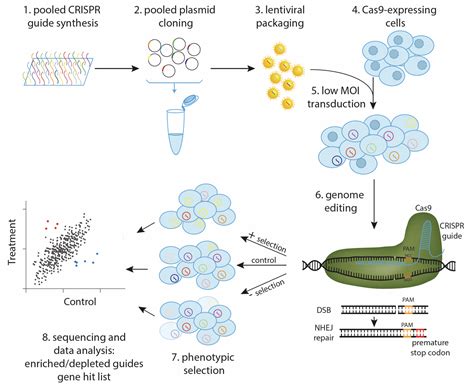
The rapid advancement of high-throughput sequencing technologies has revolutionized the field of genomics, enabling researchers to generate vast amounts of genomic data at an unprecedented scale. However, the sheer volume of data poses significant challenges in terms of analysis, interpretation, and application. Functional genomics, a field that combines genetics, molecular biology, and bioinformatics, has emerged as a crucial approach to make sense of the genomic data deluge. In this article, we will explore seven ways to apply functional genomic analysis to gain insights into the intricate relationships between genes, proteins, and cellular processes.
1. Identifying Gene Function and Regulation
Functional genomics analysis can be used to identify the functions of previously uncharacterized genes and understand how they are regulated. By integrating data from various sources, such as gene expression, protein-protein interactions, and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq), researchers can reconstruct gene regulatory networks (GRNs) that elucidate the complex interactions between transcription factors, genes, and other regulatory elements.
🔍 Note: GRNs can be used to identify potential therapeutic targets for diseases, such as cancer, where gene regulation is often disrupted.
2. Understanding Gene-Environment Interactions
Functional genomics can be used to investigate how environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or changes in diet, influence gene expression and cellular processes. By analyzing gene expression profiles in response to different environmental conditions, researchers can identify genes and pathways that are sensitive to environmental perturbations.
- Example: A study using functional genomics analysis identified genes involved in the response to arsenic exposure in human cells, providing insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying arsenic toxicity.
3. Deciphering the Molecular Basis of Disease
Functional genomics analysis can be applied to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying human diseases, such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases. By integrating data from various sources, including genome-wide association studies (GWAS), gene expression, and protein-protein interactions, researchers can identify key genes and pathways involved in disease pathogenesis.
- Example: A functional genomics analysis of Alzheimer’s disease identified several genes involved in the regulation of amyloid-β production, a hallmark of the disease.
4. Developing Personalized Medicine Approaches
Functional genomics analysis can be used to develop personalized medicine approaches tailored to an individual’s unique genetic profile. By analyzing gene expression profiles and genetic variants, researchers can identify potential therapeutic targets and predict an individual’s response to different treatments.
💊 Note: Personalized medicine approaches can improve treatment outcomes and reduce adverse reactions by tailoring therapies to an individual's specific genetic profile.
5. Improving Crop Yields and Plant Breeding
Functional genomics analysis can be applied to improve crop yields and plant breeding by identifying genes and pathways involved in key agronomic traits, such as drought tolerance and disease resistance.
- Example: A functional genomics analysis of maize identified several genes involved in drought tolerance, providing insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying this complex trait.
6. Elucidating the Microbiome's Role in Human Health
Functional genomics analysis can be used to investigate the role of the microbiome in human health and disease. By analyzing metagenomic data, researchers can identify key microbial genes and pathways involved in various diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease and obesity.
- Example: A functional genomics analysis of the gut microbiome identified several genes involved in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which play a crucial role in maintaining gut health.
7. Informing Synthetic Biology Approaches

Functional genomics analysis can be used to inform synthetic biology approaches, such as the design of novel biological pathways and circuits. By analyzing gene regulatory networks and metabolic pathways, researchers can identify key genes and regulatory elements that can be used to construct novel biological systems.
🔧 Note: Synthetic biology approaches can be used to develop novel biofuels, bioproducts, and pharmaceuticals, as well as improve existing industrial processes.
By applying functional genomics analysis to various fields, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate relationships between genes, proteins, and cellular processes. This knowledge can be used to develop novel therapeutic approaches, improve crop yields, and inform synthetic biology approaches, ultimately leading to significant advances in human health, agriculture, and biotechnology.
The key takeaways from this article are:
- Functional genomics analysis can be used to identify gene function and regulation, understand gene-environment interactions, and decipher the molecular basis of disease.
- This approach can also be used to develop personalized medicine approaches, improve crop yields, and elucidate the microbiome’s role in human health.
- Synthetic biology approaches can be informed by functional genomics analysis to design novel biological pathways and circuits.
By embracing functional genomics analysis, researchers can unlock the secrets of genomes and make significant contributions to various fields, ultimately leading to improved human health, sustainable agriculture, and innovative biotechnologies.
What is functional genomics analysis?
+
Functional genomics analysis is a field that combines genetics, molecular biology, and bioinformatics to make sense of genomic data and understand the relationships between genes, proteins, and cellular processes.
What are some applications of functional genomics analysis?
+
Functional genomics analysis has various applications, including identifying gene function and regulation, understanding gene-environment interactions, deciphering the molecular basis of disease, developing personalized medicine approaches, improving crop yields, and elucidating the microbiome’s role in human health.
How can functional genomics analysis inform synthetic biology approaches?
+
Functional genomics analysis can inform synthetic biology approaches by identifying key genes and regulatory elements that can be used to construct novel biological systems, such as novel biological pathways and circuits.



