Minimum Age to Join Military: 5 Essential Facts

Understanding the Minimum Age to Join Military: A Comprehensive Guide

Joining the military can be a life-changing decision, and for many young individuals, it’s a crucial step towards building a career, serving their country, and developing valuable skills. However, before embarking on this journey, it’s essential to understand the minimum age requirements to join the military. In this article, we’ll delve into the five essential facts about the minimum age to join the military, exploring the requirements, benefits, and considerations for prospective recruits.
Fact #1: Minimum Age Requirements Vary by Branch and Type of Service

The minimum age to join the military varies depending on the branch of service and the type of service you’re interested in. Here’s a breakdown of the minimum age requirements for each branch:
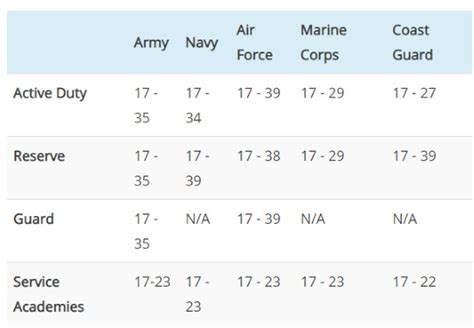
- Army: 17 years old (with parental consent) or 18 years old (without parental consent)
- Navy: 17 years old (with parental consent) or 18 years old (without parental consent)
- Air Force: 17 years old (with parental consent) or 18 years old (without parental consent)
- Marine Corps: 17 years old (with parental consent) or 18 years old (without parental consent)
- Coast Guard: 17 years old (with parental consent) or 18 years old (without parental consent)
- National Guard: 17 years old (with parental consent) or 18 years old (without parental consent)
- Reserves: 17 years old (with parental consent) or 18 years old (without parental consent)
It’s worth noting that some branches have different age requirements for certain programs, such as the Army’s Junior Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (JROTC) or the Navy’s Nuclear Field program.
Fact #2: Benefits of Joining at a Younger Age

Joining the military at a younger age can have its advantages. Some of the benefits include:
- Education Benefits: The military offers various education benefits, such as the GI Bill, which can help pay for college tuition and other educational expenses.
- Career Advancement: Joining the military at a younger age can provide a head start on your career, with opportunities for advancement and promotion.
- Personal Growth: Military service can be a transformative experience, teaching valuable skills, discipline, and leadership.
- Service Opportunities: The military offers a range of service opportunities, from combat and humanitarian missions to peacekeeping and disaster relief.
📝 Note: While joining at a younger age can have its benefits, it's essential to consider the potential risks and challenges associated with military service.
Fact #3: Medical and Physical Requirements

In addition to meeting the minimum age requirements, prospective recruits must also meet the medical and physical standards for military service. These requirements include:
- Medical Screening: Recruits must undergo a medical screening to ensure they’re fit for service.
- Physical Fitness Test: Recruits must pass a physical fitness test, which assesses their endurance, strength, and agility.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): Recruits must meet the military’s BMI standards, which vary by branch and age.
Fact #4: Enlistment Process and Requirements

The enlistment process typically involves the following steps:
- Meet with a Recruiter: Prospective recruits meet with a recruiter to discuss their options and determine their eligibility.
- Take the ASVAB Test: Recruits must take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, which assesses their aptitude and skills.
- Complete Medical Screening: Recruits undergo a medical screening to ensure they’re fit for service.
- Pass the Physical Fitness Test: Recruits must pass a physical fitness test.
- Attend Basic Training: Recruits attend basic training, also known as boot camp, where they learn the skills and values necessary for military service.
Fact #5: Considerations for Prospective Recruits

Before joining the military, prospective recruits should consider the following:
- Service Commitment: Military service requires a commitment of several years, with some contracts lasting up to six years.
- Deployment: Military personnel may be deployed to combat zones or other areas of conflict.
- Injury or Death: Military service carries inherent risks, including the risk of injury or death.
- Post-Service Benefits: The military offers various benefits for veterans, including education and employment assistance.
📝 Note: It's essential to carefully consider these factors before making a decision to join the military.
| Branch | Minimum Age (with parental consent) | Minimum Age (without parental consent) |
|---|---|---|
| Army | 17 years old | 18 years old |
| Navy | 17 years old | 18 years old |
| Air Force | 17 years old | 18 years old |
| Marine Corps | 17 years old | 18 years old |
| Coast Guard | 17 years old | 18 years old |
| National Guard | 17 years old | 18 years old |
| Reserves | 17 years old | 18 years old |
In conclusion, understanding the minimum age requirements to join the military is crucial for prospective recruits. By considering the benefits, medical and physical requirements, enlistment process, and service commitment, individuals can make informed decisions about their future. Whether you’re looking to serve your country, advance your career, or develop valuable skills, the military can be a rewarding and challenging path.
What is the minimum age to join the military?

+
The minimum age to join the military varies depending on the branch of service and the type of service. Generally, the minimum age is 17 years old with parental consent or 18 years old without parental consent.
What are the medical and physical requirements for military service?

+
Prospective recruits must meet the medical and physical standards for military service, which include a medical screening, physical fitness test, and body mass index (BMI) requirements.
What is the enlistment process like?

+
The enlistment process typically involves meeting with a recruiter, taking the ASVAB test, completing a medical screening, passing a physical fitness test, and attending basic training.



