Jet Engine Diagram: A Simplified Illustrated Guide
Understanding the Basics of a Jet Engine
A jet engine is a complex piece of machinery that powers an aircraft by generating thrust. At its core, a jet engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses the principle of jet propulsion to generate forward motion. In this article, we will break down the components of a jet engine and provide a simplified illustrated guide to help you understand how it works.
Major Components of a Jet Engine
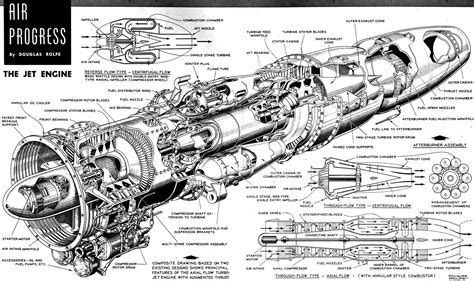
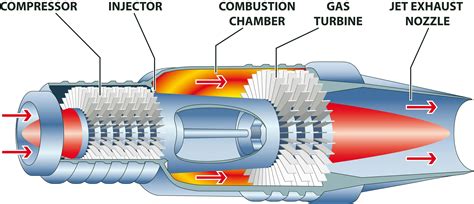
A typical jet engine consists of the following major components:
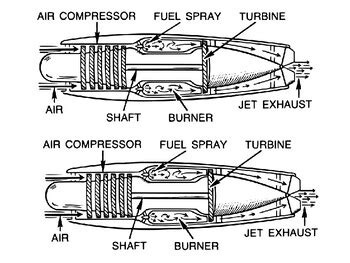
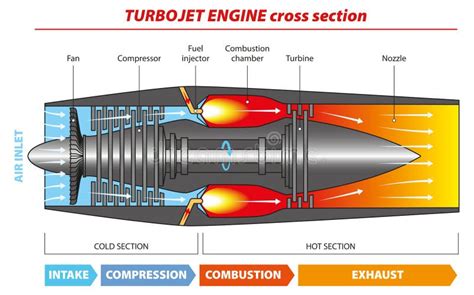
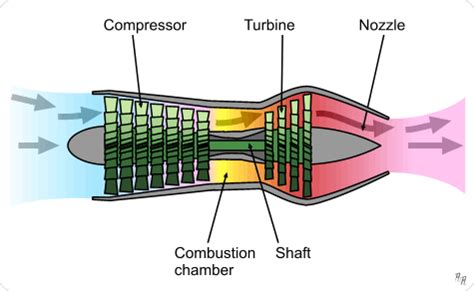
- Compressor: This is the section of the engine that draws in air and compresses it. The compressor is made up of multiple blades that spin at high speed, increasing the air pressure as it moves through the engine.
- Combustion Chamber: Also known as the combustion can or flame tube, this is where the fuel is mixed with the compressed air and ignited. The resulting explosion produces a high-pressure and high-temperature gas.
- Turbine: The turbine is driven by the hot gas produced in the combustion chamber. As the gas expands through the turbine, it spins the turbine blades, which in turn drive the compressor and the fan (if equipped).
- Nozzle: The nozzle is where the hot gas is accelerated to high speed, producing a high-velocity exhaust that generates the thrust.
- Fan (optional): Some jet engines have a fan at the front, which provides additional thrust by accelerating a large volume of air rearward.
A Simplified Illustrated Guide to a Jet Engine

Here is a simplified diagram of a jet engine:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Compressor | Draws in air and compresses it |
| 2. Combustion Chamber | Mixes fuel with compressed air and ignites it |
| 3. Turbine | Driven by hot gas, spins turbine blades |
| 4. Nozzle | Accelerates hot gas to high speed, producing thrust |
| 5. Fan (optional) | Provides additional thrust by accelerating air |
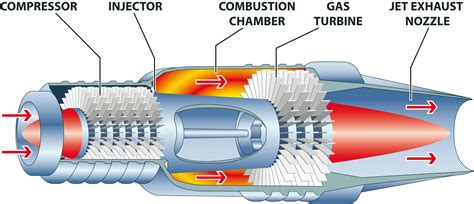
How a Jet Engine Works
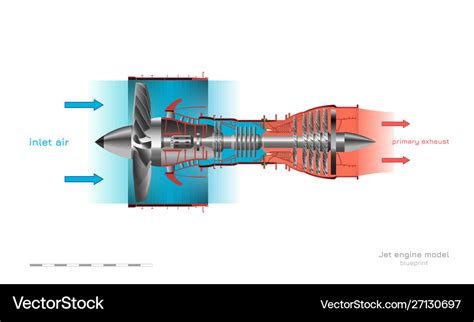
Here is a step-by-step explanation of how a jet engine works:
- Air Intake: Air is drawn into the engine through the inlet.
- Compression: The air is compressed by the compressor blades, increasing its pressure and temperature.
- Fuel Injection: Fuel is injected into the combustion chamber, where it is mixed with the compressed air.
- Ignition: The fuel-air mixture is ignited, producing a high-pressure and high-temperature gas.
- Expansion: The hot gas expands through the turbine, spinning the turbine blades.
- Nozzle: The hot gas is accelerated to high speed through the nozzle, producing a high-velocity exhaust.
- Thrust: The exhaust gases produce a forward force, propelling the aircraft forward.
🚨 Note: This is a simplified explanation, and actual jet engines are much more complex and have many additional components and systems.
Types of Jet Engines

There are several types of jet engines, including:
- Turbojet: A basic jet engine with a compressor, combustion chamber, turbine, and nozzle.
- Turbofan: A jet engine with a fan at the front, which provides additional thrust.
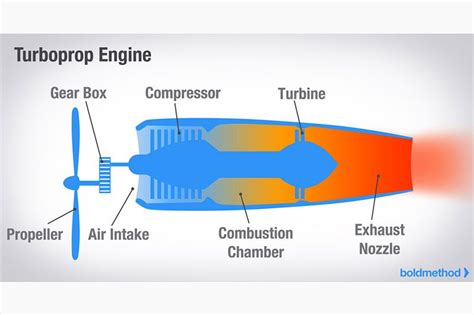
- Turboprop: A jet engine that uses a propeller to provide thrust.
- Ramjet: A jet engine that uses the atmosphere as the oxidizer, rather than carrying its own oxygen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a jet engine is a complex machine that powers an aircraft by generating thrust. By understanding the major components and how they work together, we can appreciate the incredible technology that goes into building these engines.
What is the main difference between a turbojet and a turbofan engine?
+
A turbojet engine does not have a fan at the front, while a turbofan engine has a fan that provides additional thrust.
How does a jet engine produce thrust?
+
A jet engine produces thrust by accelerating a large volume of air rearward, which produces a forward force.
What is the function of the nozzle in a jet engine?
+
The nozzle accelerates the hot gas produced in the combustion chamber to high speed, producing a high-velocity exhaust that generates thrust.



