Military Officer Rankings Chart Explained

Military Officer Rankings: Understanding the Chain of Command

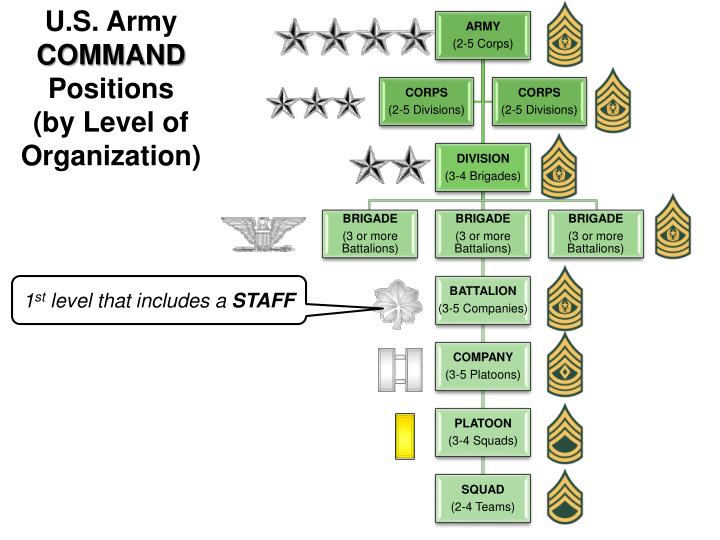
The military is a highly structured organization with a clear chain of command. At the heart of this structure are the officer rankings, which define the roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority within the armed forces. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of military officer rankings, exploring the different levels, their corresponding responsibilities, and how they fit into the overall command structure.
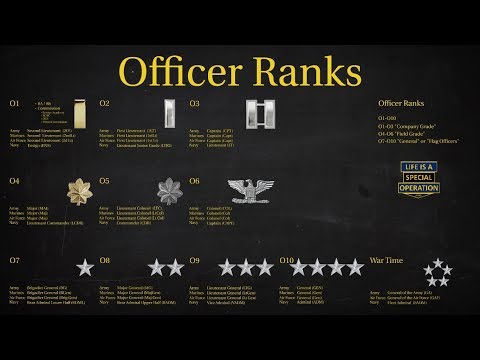
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Commissioned officers are the leaders of the military, holding positions of authority and responsibility. They are typically college-educated and have completed Officer Candidate School (OCS) or a service academy. The commissioned officer ranks are as follows:
| Rank | Insignia | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Second Lieutenant (2LT) | Entry-level officer rank, typically serving as platoon leaders or executive officers. | |
| First Lieutenant (1LT) | Junior officer rank, often serving as platoon leaders or company executive officers. | |
| Captain (CPT) | Company-grade officer rank, typically serving as company commanders or staff officers. | |
| Major (MAJ) | Field-grade officer rank, often serving as battalion executive officers or staff officers. | |
| Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) | Field-grade officer rank, typically serving as battalion commanders or staff officers. | |
| Colonel (COL) | Senior field-grade officer rank, often serving as brigade commanders or staff officers. | |
| Brigadier General (BG) | One-star general officer rank, typically serving as brigade commanders or staff officers. | |
| Major General (MG) | Two-star general officer rank, often serving as division commanders or staff officers. | |
| Lieutenant General (LTG) | Three-star general officer rank, typically serving as corps commanders or staff officers. | |
| General (GEN) | Four-star general officer rank, often serving as army commanders or staff officers. |

Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts in their field, holding specialized roles within the military. They are typically non-commissioned officers who have completed specialized training and have demonstrated expertise in their field. The warrant officer ranks are as follows:
| Rank | Insignia | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) | Entry-level warrant officer rank, typically serving as technical experts or instructors. | |
| Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) | Junior warrant officer rank, often serving as technical experts or trainers. | |
| Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) | Senior warrant officer rank, typically serving as technical experts or advisors. | |
| Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) | Senior warrant officer rank, often serving as technical experts or leaders. | |
| Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) | Master warrant officer rank, typically serving as technical experts or senior leaders. |
Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks

Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) are the backbone of the military, providing leadership and guidance to junior personnel. They are typically enlisted personnel who have completed advanced training and have demonstrated leadership potential. The NCO ranks are as follows:
| Rank | Insignia | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Corporal (CPL) | Junior NCO rank, typically serving as team leaders or squad leaders. | |
| Sergeant (SGT) | Junior NCO rank, often serving as squad leaders or platoon sergeants. | |
| Staff Sergeant (SSG) | Senior NCO rank, typically serving as platoon sergeants or section leaders. | |
| Sergeant First Class (SFC) | Senior NCO rank, often serving as platoon leaders or section leaders. | |
| Master Sergeant (MSG) | Senior NCO rank, typically serving as senior enlisted leaders or advisors. | |
| Sergeant Major (SGM) | Senior NCO rank, often serving as senior enlisted leaders or command sergeants major. |
💡 Note: The ranks and insignia may vary slightly between branches of the military, but the overall structure and hierarchy remain the same.
Conclusion
Understanding the military officer rankings is crucial for navigating the complex world of the armed forces. From the junior ranks of second lieutenant and corporal to the senior ranks of general and sergeant major, each level has its unique responsibilities and levels of authority. By grasping the hierarchy of the military, individuals can better appreciate the roles and sacrifices of military personnel and the importance of their service.
What is the highest rank in the military?

+
The highest rank in the military is General (GEN) or Admiral (ADM) in the Navy.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?

+
A commissioned officer is a college-educated leader who holds a position of authority, while a warrant officer is a technical expert in their field, often serving as instructors or advisors.
What is the role of a non-commissioned officer (NCO)?

+
NCOs provide leadership and guidance to junior personnel, serving as team leaders, squad leaders, or platoon sergeants.



