7 Key Benefits of National Guard vs Army

National Guard vs Army: Understanding the Difference

When considering a career in the military, many individuals are torn between joining the National Guard and the Army. Both offer unique benefits and opportunities for service, but there are key differences between the two. In this article, we will explore the 7 key benefits of National Guard vs Army, to help you make an informed decision.
1. Service Commitment

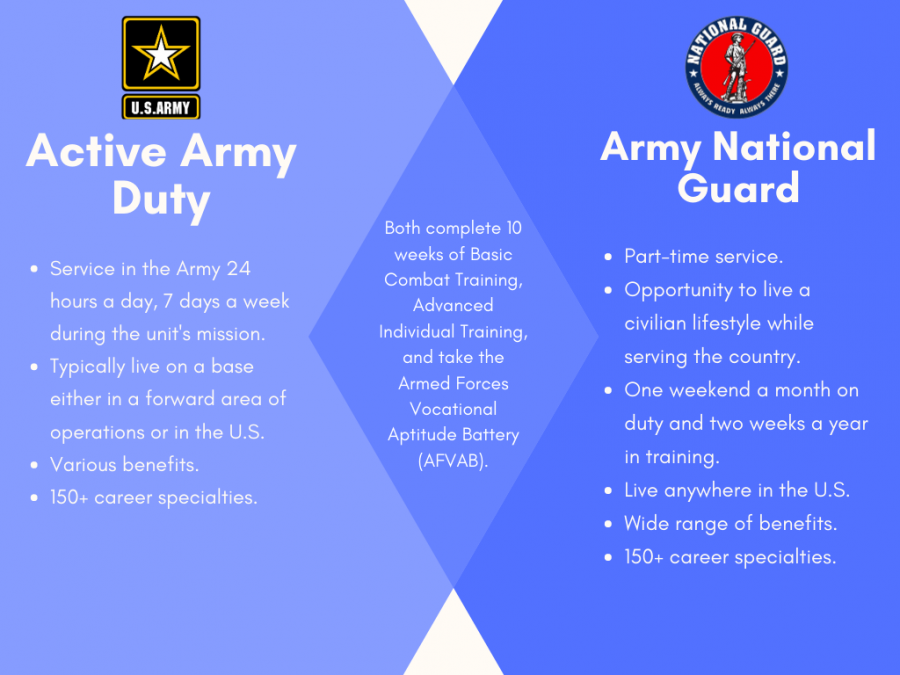
One of the primary differences between the National Guard and the Army is the service commitment. The National Guard requires a six-year commitment, with one weekend of drill per month and two weeks of annual training. In contrast, the Army requires a minimum of two years of active duty service, followed by four years in the reserves.
- National Guard: 6-year commitment, with one weekend of drill per month and two weeks of annual training
- Army: Minimum 2 years active duty, followed by 4 years in reserves
2. Deployment Frequency
Deployment frequency is another significant difference between the National Guard and the Army. National Guard units are typically deployed for shorter periods, usually 6-12 months, whereas Army units can be deployed for longer periods, often 12-18 months.
- National Guard: Typically deployed for 6-12 months
- Army: Typically deployed for 12-18 months
3. Education Benefits

Both the National Guard and the Army offer education benefits, but the National Guard’s benefits are more generous. The National Guard offers up to 100% tuition assistance, while the Army offers up to 80% tuition assistance.
- National Guard: Up to 100% tuition assistance
- Army: Up to 80% tuition assistance
4. Career Opportunities

The National Guard and the Army both offer a wide range of career opportunities, but the National Guard is more focused on domestic missions, such as disaster relief and homeland security. The Army, on the other hand, is more focused on international missions and combat operations.
- National Guard: Focused on domestic missions, such as disaster relief and homeland security
- Army: Focused on international missions and combat operations
5. Pay and Benefits

Pay and benefits are similar between the National Guard and the Army, but the National Guard offers more opportunities for additional income through drill pay and annual training pay.
- National Guard: Offers drill pay and annual training pay, in addition to base pay
- Army: Offers base pay and benefits, with limited opportunities for additional income
6. Training and Experience

Both the National Guard and the Army offer comprehensive training and experience, but the National Guard’s training is more focused on domestic missions and homeland security. The Army’s training is more focused on combat operations and international missions.
- National Guard: Training focused on domestic missions and homeland security
- Army: Training focused on combat operations and international missions
7. Work-Life Balance

Finally, the National Guard offers a better work-life balance than the Army, with more opportunities for civilians to maintain a career and family life while serving.
- National Guard: Offers a better work-life balance, with more opportunities for civilians to maintain a career and family life
- Army: Offers a more demanding schedule, with limited opportunities for civilians to maintain a career and family life
💡 Note: The benefits and differences between the National Guard and the Army may vary depending on individual circumstances and career choices.
In conclusion, the National Guard and the Army both offer unique benefits and opportunities for service, but the National Guard’s benefits are more focused on domestic missions, education, and work-life balance. Ultimately, the choice between the National Guard and the Army depends on individual priorities and career goals.
What is the main difference between the National Guard and the Army?

+
The main difference between the National Guard and the Army is the service commitment. The National Guard requires a six-year commitment, with one weekend of drill per month and two weeks of annual training, whereas the Army requires a minimum of two years of active duty service, followed by four years in the reserves.
Which branch offers more education benefits?

+
The National Guard offers more education benefits, with up to 100% tuition assistance, whereas the Army offers up to 80% tuition assistance.
What is the focus of the National Guard’s training?

+
The National Guard’s training is focused on domestic missions and homeland security.