5 Ways to Identify Persistent Pupillary Membrane

The identification of Persistent Pupillary Membrane (PPM) is crucial in ophthalmic diagnosis, as it can have significant implications for vision and eye health. A PPM is a congenital anomaly where a remnant of the embryological pupillary membrane persists into adulthood. Here are 5 ways to identify PPM:
Understanding the Anatomy of PPM
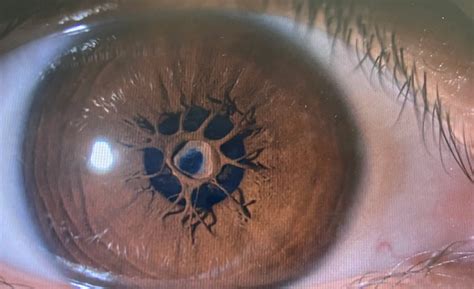
Before we dive into the methods of identification, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of PPM. A PPM is a thin, fibrovascular membrane that originates from the iris collarette and inserts into the edge of the pupil. It can be unilateral or bilateral and may be associated with other ocular anomalies.
1. Slit-Lamp Biomicroscopy
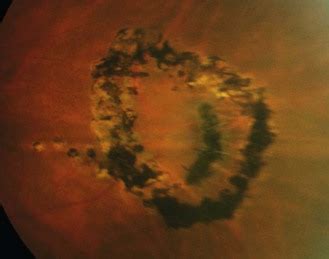
Slit-lamp biomicroscopy is the primary method for identifying PPM. A slit lamp provides a stereoscopic view of the anterior segment, allowing for a detailed examination of the iris and pupil. During the examination, the following features may be observed:
- A thin, grayish-white membrane extending from the iris collarette to the edge of the pupil
- A translucent or semi-transparent appearance, which may be more prominent against the background of the iris
- A membrane that may be irregular, wispy, or feathery in appearance
👀 Note: A thorough slit-lamp examination requires proper training and experience to accurately identify PPM.
2. High-Magnification Photography
High-magnification photography, such as anterior segment photography or optical coherence tomography (OCT), can help confirm the presence of PPM. These images can provide a detailed view of the iris and pupil, highlighting the membrane’s morphology.
3. Iris Transillumination
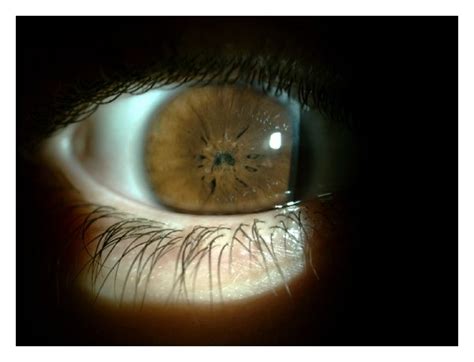
Iris transillumination is a technique that involves shining a light through the iris to visualize the pupil and surrounding structures. In cases of PPM, the membrane may appear as a translucent or semi-transparent area within the iris.
4. Gonioscopy
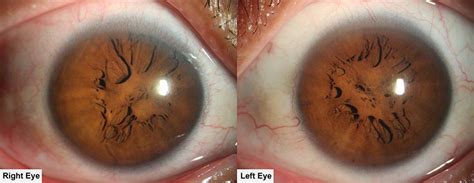
Gonioscopy is an examination technique that allows for visualization of the iridocorneal angle and the anterior segment. During gonioscopy, the presence of PPM may be observed as a thin membrane extending from the iris to the pupil.
5. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)

OCT is a non-invasive imaging modality that provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of the anterior segment. OCT can help confirm the presence of PPM and evaluate its morphology, including the thickness and insertion points of the membrane.
| Identification Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Slit-Lamp Biomicroscopy | Provides a stereoscopic view of the anterior segment for detailed examination of the iris and pupil |
| High-Magnification Photography | Confirms the presence of PPM through high-magnification images of the iris and pupil |
| Iris Transillumination | Visualizes the pupil and surrounding structures, highlighting the membrane's morphology |
| Gonioscopy | Allows for visualization of the iridocorneal angle and anterior segment, including the presence of PPM |
| Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) | Provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of the anterior segment to confirm PPM and evaluate its morphology |
In conclusion, identifying PPM requires a combination of clinical examination techniques and imaging modalities. By understanding the anatomy of PPM and utilizing these 5 methods, ophthalmologists can accurately diagnose and manage this congenital anomaly.
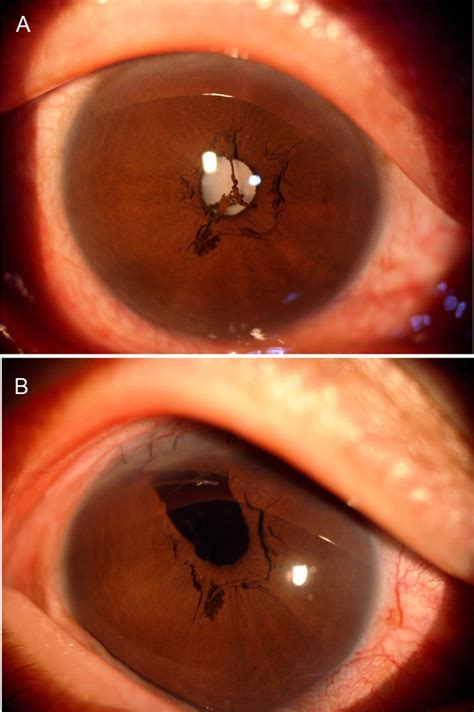
What is Persistent Pupillary Membrane (PPM)?
+
Persistent Pupillary Membrane (PPM) is a congenital anomaly where a remnant of the embryological pupillary membrane persists into adulthood.
How is PPM diagnosed?

+
PPM can be diagnosed through a combination of clinical examination techniques, including slit-lamp biomicroscopy, high-magnification photography, iris transillumination, gonioscopy, and optical coherence tomography (OCT).
What are the implications of PPM for vision and eye health?
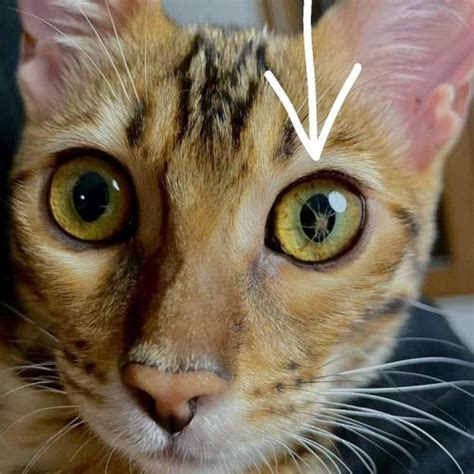

+
PPM can have significant implications for vision and eye health, including vision loss, eye pain, and increased risk of eye infections.