7 Ways to Reverse Pre Diabetes with Diet

Reversing Pre-Diabetes through Dietary Changes: A Comprehensive Guide

Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is a warning sign that diabetes may develop in the future if left unchecked. However, with dietary changes, it is possible to reverse pre-diabetes and prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes. In this article, we will explore seven ways to reverse pre-diabetes through diet.
Understanding Pre-Diabetes

Pre-diabetes, also known as impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or impaired fasting glucose (IFG), is a condition where the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. As a result, blood sugar levels rise, and the pancreas produces more insulin to compensate. Over time, this can lead to pancreatic exhaustion, and the development of type 2 diabetes.
Dietary Changes to Reverse Pre-Diabetes

Reversing pre-diabetes requires a multi-faceted approach that includes dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss. Here are seven dietary changes that can help reverse pre-diabetes:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet

Eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help regulate blood sugar levels. Aim to include a variety of colors on your plate to ensure you are getting a range of nutrients.
🥗 Note: Focus on whole foods rather than processed and packaged foods, which are often high in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats.
2. Choose Low Glycemic Index Foods
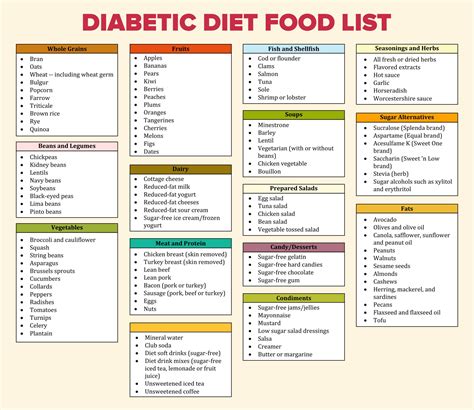
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Choosing low GI foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent spikes.
| Food | Glycemic Index |
|---|---|
| White bread | High (70-80) |
| Whole wheat bread | Low (30-40) |
| Apple | Low (30-40) |
| Potato | Medium (50-60) |

3. Increase Fiber Intake

Fiber is an essential nutrient that can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote satiety. Aim to include a variety of high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, in your diet.
- Fruits: berries, apples, bananas
- Vegetables: broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes
- Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread
- Legumes: lentils, chickpeas, black beans
4. Stay Hydrated

Staying hydrated is essential for overall health, and can also help regulate blood sugar levels. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, and avoid sugary drinks, such as soda and sports drinks.
💧 Note: Monitor your urine output to ensure you are drinking enough water. If your urine is dark yellow or you are not urinating frequently enough, it may be a sign that you are not drinking enough water.
5. Limit Added Sugars
Added sugars, such as those found in sugary drinks, baked goods, and processed snacks, can raise blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance. Aim to limit added sugars to less than 10% of your daily calorie intake.
6. Choose Healthy Fats

Healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote satiety. Aim to include a variety of healthy fats in your diet.
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, walnuts, chia seeds
- Avocados
- Olive oil
7. Watch Portion Sizes

Watching portion sizes is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and regulating blood sugar levels. Use a food scale or measuring cups to measure your food portions, and avoid eating in front of screens or while doing other activities.
🍴 Note: Eat slowly and mindfully to ensure you are satisfied with your meal and not overeating.
Reversing pre-diabetes requires a long-term commitment to healthy lifestyle choices, including dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss. By incorporating these seven dietary changes into your daily routine, you can help regulate blood sugar levels, prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes, and maintain overall health and well-being.
What is pre-diabetes?

+
Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Can pre-diabetes be reversed?

+
What are the symptoms of pre-diabetes?

+
Pre-diabetes often does not have any noticeable symptoms, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems.



