Pricing Public Health: The True Cost of Wellness
Understanding the Economics of Public Health

The concept of public health has become increasingly important in recent years, as governments and healthcare systems around the world grapple with the challenges of providing affordable and effective healthcare to their populations. One of the key issues in public health is the question of pricing - how much should individuals and governments pay for healthcare services, and what are the economic implications of different pricing models?
The True Cost of Wellness
The cost of healthcare is a complex issue, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. However, by examining the different factors that contribute to the cost of healthcare, we can begin to understand the true cost of wellness.
- Direct Costs: These include the costs of healthcare services, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications. Direct costs are typically paid for by individuals or governments through insurance premiums, out-of-pocket payments, or taxes.
- Indirect Costs: These include the costs of lost productivity, transportation, and other expenses associated with seeking healthcare. Indirect costs can be significant, particularly for individuals with chronic conditions or those who require ongoing care.
- Opportunity Costs: These include the costs of not investing in other areas of public health, such as prevention and education. Opportunity costs can be significant, particularly if funds are diverted from effective programs to pay for expensive treatments.
Factors Affecting Public Health Pricing

Several factors can affect public health pricing, including:
- Supply and Demand: The availability of healthcare services and the demand for them can impact pricing. In areas with limited healthcare providers, prices may be higher due to reduced competition.
- Government Policies: Government policies, such as pricing regulations and reimbursement rates, can impact the cost of healthcare.
- Technological Advances: New technologies and treatments can increase the cost of healthcare, but may also improve health outcomes.
- Demographic Changes: Changes in population demographics, such as aging or urbanization, can impact the demand for healthcare services and pricing.
Pricing Models in Public Health

There are several pricing models used in public health, including:
- Fee-for-Service: This model involves paying healthcare providers for each service they provide, regardless of the outcome.
- Capitation: This model involves paying healthcare providers a fixed fee for each patient they care for, regardless of the services provided.
- Value-Based Pricing: This model involves paying healthcare providers based on the value of the services they provide, such as improved health outcomes.
🤔 Note: The choice of pricing model can have significant implications for public health outcomes and costs. For example, fee-for-service models can incentivize healthcare providers to provide more services, which may not always be necessary or effective.
Examples of Public Health Pricing in Action
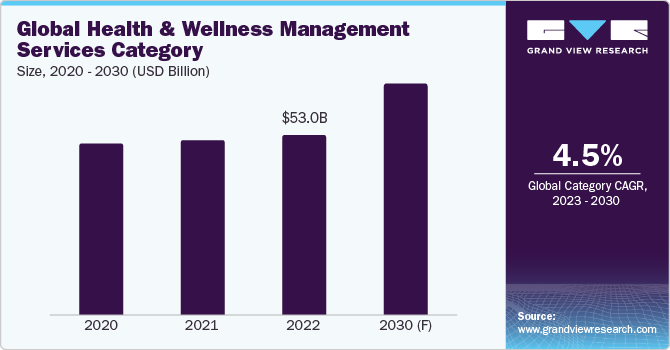
- The UK’s National Health Service (NHS): The NHS uses a combination of fee-for-service and capitation models to pay healthcare providers.
- The US’s Medicare Program: Medicare uses a fee-for-service model to pay healthcare providers, but is also exploring value-based pricing models.
- Singapore’s Healthcare System: Singapore’s healthcare system uses a combination of fee-for-service and value-based pricing models to pay healthcare providers.
Conclusion

Pricing public health is a complex issue, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. By understanding the different factors that contribute to the cost of healthcare and examining different pricing models, we can begin to develop effective solutions that promote wellness and reduce healthcare costs.
The true cost of wellness is more than just the direct costs of healthcare services - it also includes indirect costs, opportunity costs, and the costs of lost productivity. By considering these factors and developing effective pricing models, we can promote better health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Key Takeaways
- Public health pricing is a complex issue that involves understanding the direct, indirect, and opportunity costs of healthcare.
- Different pricing models, such as fee-for-service, capitation, and value-based pricing, can have significant implications for public health outcomes and costs.
- Effective pricing models must consider the value of healthcare services, as well as the costs and outcomes associated with them.
What is the difference between fee-for-service and value-based pricing models?

+
Fee-for-service models involve paying healthcare providers for each service they provide, regardless of the outcome. Value-based pricing models involve paying healthcare providers based on the value of the services they provide, such as improved health outcomes.
What are some examples of public health pricing models in action?

+
The UK’s National Health Service (NHS), the US’s Medicare Program, and Singapore’s healthcare system are all examples of public health pricing models in action.
What are some of the factors that affect public health pricing?

+
Supply and demand, government policies, technological advances, and demographic changes are all factors that can affect public health pricing.