Systemic Racism by the Numbers: Quantitative Data Revealed

Understanding Systemic Racism through Quantitative Data

Systemic racism is a pervasive and complex issue that affects various aspects of society, from education and employment to healthcare and housing. While it can be challenging to grasp the scope of this problem, quantitative data provides valuable insights into the disparities faced by marginalized communities. This article delves into the numbers, highlighting key statistics that illustrate the extent of systemic racism in different areas.
Economic Disparities
Economic inequality is a significant aspect of systemic racism. The following statistics demonstrate the disparities in wealth, income, and employment opportunities:
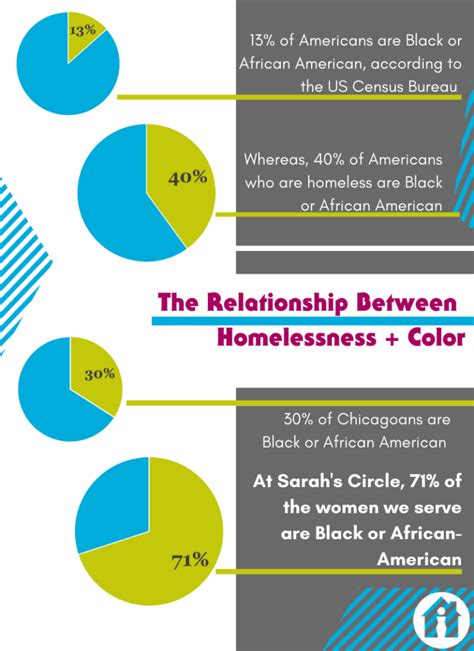
- Wealth Gap: The median wealth of white families in the United States is 171,000, compared to 17,600 for Black families and $20,700 for Hispanic families (Federal Reserve, 2019).
- Income Inequality: In 2020, the median income for white households was 76,057, while for Black households it was 43,862, and for Hispanic households it was $52,883 (U.S. Census Bureau, 2020).
- Employment Opportunities: Black and Hispanic workers are more likely to experience unemployment, with rates of 6.8% and 5.5%, respectively, compared to 3.8% for white workers (Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2022).
Education and Academic Achievement

Systemic racism also affects education, leading to disparities in academic achievement and opportunities:
- High School Graduation Rates: In 2019, the high school graduation rate for white students was 91%, compared to 79% for Black students and 81% for Hispanic students (National Center for Education Statistics, 2020).
- College Enrollment: In 2020, 43% of white high school graduates enrolled in college, compared to 34% of Black graduates and 36% of Hispanic graduates (National Center for Education Statistics, 2020).
- Teacher Diversity: In 2017-2018, only 18% of public school teachers were teachers of color, despite students of color making up 50% of the student population (National Center for Education Statistics, 2019).
Healthcare Disparities

Systemic racism affects healthcare outcomes, leading to disparities in access to care, health insurance, and mortality rates:
- Health Insurance: In 2020, 8.8% of white individuals lacked health insurance, compared to 12.1% of Black individuals and 17.9% of Hispanic individuals (U.S. Census Bureau, 2020).
- Mortality Rates: In 2020, the mortality rate for Black infants was 2.5 times higher than for white infants, while the mortality rate for Hispanic infants was 1.5 times higher (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020).
- Chronic Disease: In 2019, 45% of Black adults and 42% of Hispanic adults had at least one chronic disease, compared to 34% of white adults (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019).
Criminal Justice System
Systemic racism is also present in the criminal justice system, leading to disparities in arrest rates, incarceration rates, and sentencing:
- Arrest Rates: In 2020, Black individuals were arrested at a rate 2.5 times higher than white individuals, while Hispanic individuals were arrested at a rate 1.5 times higher (Federal Bureau of Investigation, 2020).
- Incarceration Rates: In 2020, the incarceration rate for Black individuals was 5.5 times higher than for white individuals, while the incarceration rate for Hispanic individuals was 3.5 times higher (Bureau of Justice Statistics, 2020).
- Sentencing: In 2019, Black defendants received sentences 19% longer than white defendants for similar crimes, while Hispanic defendants received sentences 12% longer (United States Sentencing Commission, 2019).
🚨 Note: These statistics are not exhaustive, and systemic racism affects many other areas, including housing, environmental justice, and voting rights.
In conclusion, quantitative data reveals the profound impact of systemic racism on various aspects of society. Understanding these disparities is crucial for developing effective solutions to address the root causes of systemic racism. By acknowledging and confronting these issues, we can work towards creating a more equitable society for all.
What is systemic racism?

+
Systemic racism refers to the embedded, institutional, and structural racism that pervades various aspects of society, including education, employment, healthcare, and the criminal justice system.
How can we address systemic racism?
+
Addressing systemic racism requires a multifaceted approach, including policy changes, education, and community engagement. It is essential to acknowledge and confront the root causes of systemic racism, working towards creating a more equitable society for all.
What can individuals do to combat systemic racism?

+
Individuals can combat systemic racism by educating themselves, engaging in respectful dialogue, and advocating for policy changes. They can also support organizations working towards racial equity and participate in community initiatives promoting social justice.



