3 Key Differences: Race vs Ethnicity vs Nationality
Understanding the Complexities of Identity: Race, Ethnicity, and Nationality
When discussing identity, three terms are often used interchangeably, but incorrectly so: race, ethnicity, and nationality. While they are related, each term has a distinct meaning and significance. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of each term and explore the key differences between them.
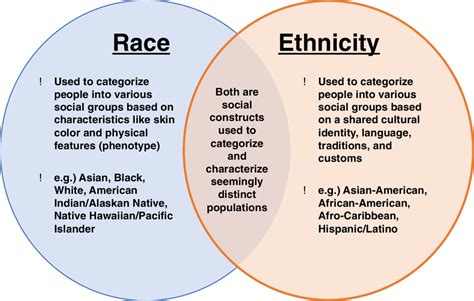
Race: A Social Construct

Definition: Race refers to the physical characteristics that distinguish one group of people from another, such as skin color, hair texture, and facial features.
Importance: The concept of race has been used to categorize and often discriminate against certain groups of people. However, it is essential to recognize that race is a social construct, not a scientific fact. There is no biological basis for the concept of race, and it has been widely discredited as a valid way to classify humans.
Example: In the United States, the concept of race has been used to categorize people into different groups, such as white, black, Asian, and Native American. However, these categories are not fixed and have changed over time.
Ethnicity: A Shared Culture and Heritage
Definition: Ethnicity refers to a shared culture, language, and heritage that defines a particular group of people.
Importance: Ethnicity is a vital aspect of a person’s identity, as it provides a sense of belonging and connection to their community. Ethnicity can be passed down through generations, and it often influences a person’s values, traditions, and customs.
Example: For instance, a person may identify as Mexican-American, which is an ethnicity that encompasses a shared culture, language, and heritage.
Nationality: Citizenship and Country of Origin

Definition: Nationality refers to a person’s citizenship and country of origin.
Importance: Nationality is often tied to a person’s sense of identity and can influence their access to resources, education, and employment opportunities.
Example: A person may be a citizen of the United States, but their nationality may be Mexican or Chinese, depending on their country of origin.
Key Differences: A Comparison
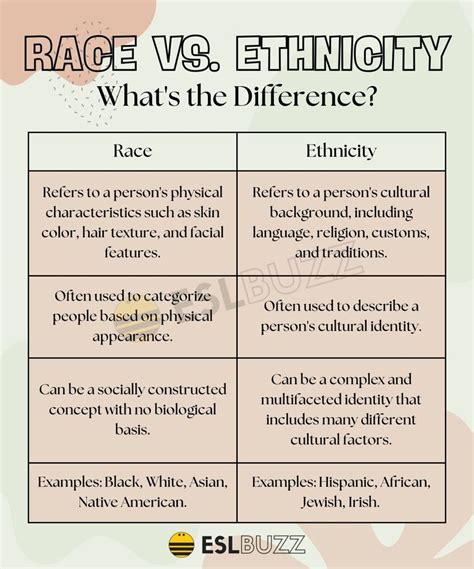
| Race | Ethnicity | Nationality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical characteristics | Shared culture and heritage | Citizenship and country of origin |
| Importance | Social construct, often used to discriminate | Vital aspect of identity, sense of belonging | Access to resources, education, and employment opportunities |
| Example | White, black, Asian, Native American | Mexican-American, Chinese-American, African-American | United States, Mexico, China |

📝 Note: The table above is a simplified representation of the key differences between race, ethnicity, and nationality. It is essential to recognize that these concepts are complex and can intersect in various ways.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding the differences between race, ethnicity, and nationality is crucial for promoting inclusivity and combating discrimination. By recognizing the nuances of each term, we can better appreciate the complexities of identity and work towards creating a more equitable society.
What is the difference between race and ethnicity?

+
Race refers to physical characteristics, while ethnicity refers to a shared culture, language, and heritage.
Can a person have multiple nationalities?

+
Yes, a person can have multiple nationalities, also known as dual or multiple citizenship.
How do race, ethnicity, and nationality intersect?

+
Race, ethnicity, and nationality can intersect in various ways, such as a person identifying as black (race), African-American (ethnicity), and a citizen of the United States (nationality).



