Army EOD Requirements: Become an Explosive Ordnance Disposal Expert

Introduction to Army EOD Requirements

The United States Army Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) team is a highly specialized group of experts who are trained to handle and dispose of explosive threats. To become an Army EOD expert, one must meet specific requirements and undergo rigorous training. In this article, we will outline the Army EOD requirements and provide an overview of the training process.
Basic Requirements
To be eligible for the Army EOD program, candidates must meet the following basic requirements:
- Be a U.S. citizen
- Be between the ages of 17 and 35
- Score a minimum of 110 on the General Technical (GT) section of the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test
- Score a minimum of 100 on the Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) section of the ASVAB test
- Have a high school diploma or equivalent
- Be able to obtain a Secret security clearance
- Be willing to serve for at least 4 years
Physical and Mental Requirements
Army EOD experts must be physically and mentally fit to perform their duties. Candidates must meet the following physical and mental requirements:
- Pass the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT) with a minimum score of 240
- Have a body mass index (BMI) of 24 or less
- Have a vision of 20⁄20 in each eye, with or without corrective lenses
- Have normal color vision
- Pass a mental evaluation to assess their suitability for EOD work
EOD Training Process

The Army EOD training process is challenging and comprehensive. It includes the following phases:
- Basic Training: New recruits attend Basic Combat Training (BCT) for 10 weeks, where they learn basic soldiering skills and physical fitness.
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): After BCT, candidates attend AIT for 24 weeks, where they learn EOD-specific skills, such as explosive theory, demolition, and bomb disposal.
- EOD School: Candidates then attend the U.S. Army Explosive Ordnance Disposal School at Fort Lee, Virginia, for 24 weeks, where they learn advanced EOD skills and techniques.
- On-the-Job Training: After completing EOD school, candidates receive on-the-job training, where they work under the supervision of experienced EOD experts.
EOD Certification

To become a certified Army EOD expert, candidates must complete the following certification process:
- EOD Certification Course: Candidates attend a 4-week EOD certification course, where they learn advanced EOD skills and techniques.
- Written Exam: Candidates must pass a written exam to demonstrate their knowledge of EOD principles and procedures.
- Practical Exam: Candidates must pass a practical exam, where they demonstrate their ability to perform EOD tasks.
💡 Note: The certification process is continuous, and EOD experts must complete regular training and certification exercises to maintain their certification.
EOD Job Description

Army EOD experts are responsible for:
- Explosive Disposal: Disposing of explosive threats, such as bombs and improvised explosive devices (IEDs)
- Explosive Ordinance Disposal: Identifying and disposing of explosive ordnance, such as artillery shells and grenades
- Bomb Disposal: Disposing of bombs and other explosive devices
- Explosive Safety: Ensuring the safe handling and storage of explosive materials
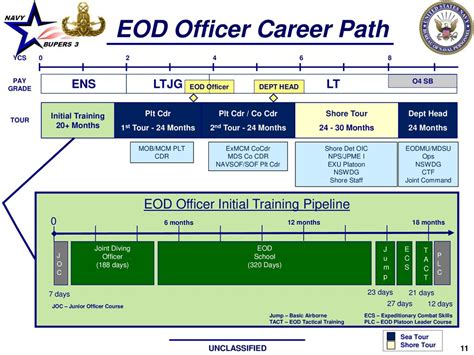
EOD Career Path

The Army EOD career path offers opportunities for advancement and specialization. EOD experts can advance to the following positions:
- EOD Team Leader: Leads an EOD team and is responsible for planning and executing EOD operations.
- EOD Squad Leader: Leads an EOD squad and is responsible for planning and executing EOD operations.
- EOD Platoon Sergeant: Leads an EOD platoon and is responsible for planning and executing EOD operations.
- EOD Company Commander: Commands an EOD company and is responsible for planning and executing EOD operations.
Conclusion

Becoming an Army EOD expert requires meeting specific requirements and undergoing rigorous training. Army EOD experts play a critical role in ensuring the safety of military personnel and civilians by disposing of explosive threats. If you are interested in pursuing a career as an Army EOD expert, we encourage you to research the requirements and training process further.
What is the minimum ASVAB score required for Army EOD?

+
The minimum ASVAB score required for Army EOD is 110 on the General Technical (GT) section and 100 on the Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) section.
How long is the Army EOD training process?

+
The Army EOD training process is approximately 52 weeks long, including Basic Training, Advanced Individual Training, and EOD School.
What is the role of an Army EOD expert?

+
Army EOD experts are responsible for disposing of explosive threats, such as bombs and improvised explosive devices (IEDs), and ensuring the safe handling and storage of explosive materials.
Related Terms:
- Army EOD physical requirements
- Army EOD Officer career path
- EOD Army death rate
- Army EOD units
- Army EOD training
- Army EOD recruiting



