Marine Sergeant Salary: A Comprehensive Breakdown

Understanding the Marine Sergeant Salary Structure

The United States Marine Corps is a prestigious branch of the military that offers a range of career opportunities for individuals who are passionate about serving their country. One of the most respected roles in the Marine Corps is that of a Sergeant, which is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank that requires a high level of leadership, technical expertise, and physical fitness. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive breakdown of the Marine Sergeant salary structure, including the factors that influence their pay, the different types of pay they receive, and the average salary ranges for Sergeants in the Marine Corps.
Factors that Influence Marine Sergeant Salary

The salary of a Marine Sergeant is influenced by several factors, including their rank, time in service, and job specialty. Here are some of the key factors that affect their pay:
- Rank: The rank of Sergeant is the third-highest NCO rank in the Marine Corps, and it is classified as an E-5 rank. The higher the rank, the higher the salary.
- Time in Service: Sergeants who have more time in service typically earn higher salaries than those who are newer to the Corps.
- Job Specialty: Marines who specialize in certain jobs, such as combat arms or aviation, may earn higher salaries than those in other specialties.
- Location: Marines who serve in certain locations, such as hazardous duty zones or remote areas, may receive additional pay for their service.
Types of Pay for Marine Sergeants

Marine Sergeants receive several types of pay, including:
- Basic Pay: This is the base salary for Sergeants, which is determined by their rank and time in service.
- Allowances: Sergeants may receive allowances for food, housing, and other expenses, depending on their location and job specialty.
- Special Pay: Marines who serve in certain jobs or locations may receive special pay, such as hazardous duty pay or jump pay.
- Bonuses: Sergeants may be eligible for bonuses, such as enlistment bonuses or reenlistment bonuses.
Average Salary Ranges for Marine Sergeants
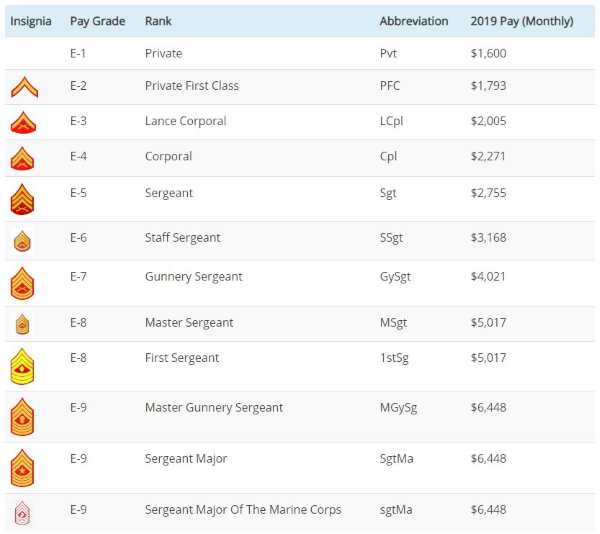
The average salary for a Marine Sergeant varies depending on their rank, time in service, and job specialty. Here are some approximate salary ranges for Sergeants in the Marine Corps:
- E-5 Sergeant (4-8 years of service): 40,000 - 60,000 per year
- E-5 Sergeant (8-12 years of service): 50,000 - 70,000 per year
- E-5 Sergeant (12-16 years of service): 60,000 - 80,000 per year
- E-5 Sergeant (16-20 years of service): 70,000 - 90,000 per year
| Rank | Time in Service | Basic Pay | Allowances | Special Pay | Total Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-5 Sergeant | 4-8 years | $35,000 - $50,000 | $5,000 - $10,000 | $2,000 - $5,000 | $42,000 - $65,000 |
| E-5 Sergeant | 8-12 years | $45,000 - $65,000 | $7,000 - $12,000 | $3,000 - $6,000 | $55,000 - $83,000 |
| E-5 Sergeant | 12-16 years | $55,000 - $75,000 | $9,000 - $15,000 | $4,000 - $8,000 | $68,000 - $98,000 |
| E-5 Sergeant | 16-20 years | $65,000 - $85,000 | $11,000 - $18,000 | $5,000 - $10,000 | $81,000 - $113,000 |

📝 Note: The salary ranges listed above are approximate and may vary depending on individual circumstances.
In conclusion, the Marine Sergeant salary structure is influenced by several factors, including rank, time in service, and job specialty. Sergeants receive several types of pay, including basic pay, allowances, special pay, and bonuses. The average salary ranges for Sergeants in the Marine Corps vary depending on their rank and time in service, but can range from 40,000 to over 100,000 per year.
What is the average salary for a Marine Sergeant?

+
The average salary for a Marine Sergeant varies depending on their rank and time in service, but can range from 40,000 to over 100,000 per year.
What factors influence the salary of a Marine Sergeant?

+
The salary of a Marine Sergeant is influenced by several factors, including their rank, time in service, and job specialty.
Do Marine Sergeants receive allowances?

+
Yes, Marine Sergeants may receive allowances for food, housing, and other expenses, depending on their location and job specialty.



