Exploring the Solar System Planets' Unique Colours

Unveiling the Vibrant Hues of Our Celestial Neighbors

The solar system is home to a diverse range of planets, each with its own unique characteristics and features. One of the most striking aspects of these celestial bodies is their distinct colors, which are shaped by a combination of factors, including atmospheric composition, temperature, and geological activity. In this article, we will embark on a journey to explore the fascinating colors of the solar system planets.
Mercury: The Scorched Grey Planet
Mercury, the smallest and innermost planet, is often described as a grey, barren world. Its surface is pockmarked with craters, indicating a geologically inactive surface that has been bombarded by asteroids and comets over billions of years. The grey coloration is a result of the planet’s surface composition, which is rich in iron and magnesium. Mercury’s proximity to the sun also means that it receives intense radiation, causing its surface to heat up and lose any volatile compounds that may have once existed.
Venus: The Thick Atmosphere of Sulphuric Acid and Droplets

Venus, often shrouded in thick clouds of sulfuric acid and droplets of sulfuric acid, appears as a bright white-yellow planet. This is due to the way that the sulfuric acid particles scatter sunlight, giving the planet a hazy appearance. However, if we were to peer beneath the clouds, we would see a surface that is actually quite dark, composed of volcanic rock and basalt. The extreme greenhouse effect caused by the thick atmosphere makes Venus the hottest planet in the solar system, with surface temperatures reaching as high as 462°C (863°F).
Earth: The Blue and White Marble
Our home planet, Earth, is characterized by its distinctive blue and white coloration, which is a result of its oceans, atmosphere, and cloud cover. The blue color comes from the absorption of red light by the oceans, while the white clouds are made up of water vapor and ice crystals. The green and brown hues that can be seen on Earth’s surface are due to the presence of vegetation and soil.
Mars: The Red Planet of Iron Oxide
Mars, often referred to as the Red Planet, gets its distinctive color from the iron oxide particles that are present in the planet’s soil and rocks. The iron oxide, also known as rust, is a result of the planet’s iron-rich composition and the oxidation of the metal over time. The red coloration is also influenced by the planet’s thin atmosphere, which scatters sunlight in a way that emphasizes the red hues.
Jupiter: The Banded Giant of Hydrogen and Helium
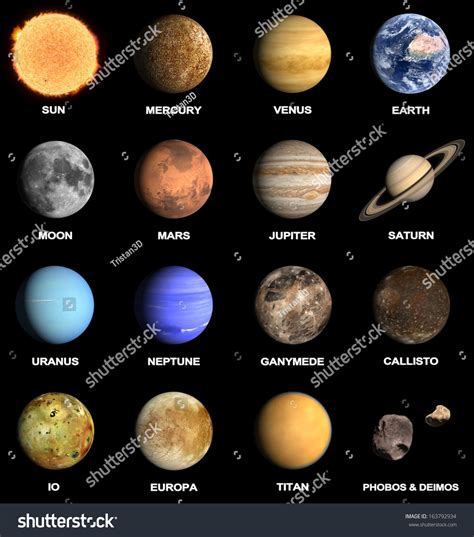

Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is known for its striking banded appearance, which is caused by the presence of different cloud layers in its atmosphere. The planet’s atmosphere is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, which create the distinct cloud bands that we see. The colors of the bands are due to the presence of different compounds, such as ammonia, water, and sulfur, which absorb and reflect sunlight in different ways.
Saturn: The Ringed Beauty of Ice and Rock
Saturn, another gas giant, is famous for its stunning ring system, which is composed of ice and rock particles. The rings appear as a bright white color due to the way that the ice particles reflect sunlight. The planet’s atmosphere is also composed of hydrogen and helium, which create the characteristic yellow-brown hue that we see.
Uranus: The Tilted Giant of Methane and Ammonia

Uranus, an icy giant, has a distinct blue-green color due to the presence of methane and ammonia in its atmosphere. The methane absorbs red light, causing the planet to appear blue, while the ammonia creates the greenish hue. The planet’s atmosphere is also composed of hydrogen and helium, which contribute to its overall color.
Neptune: The Farthest Reach of Methane and Water

Neptune, the farthest planet from the sun, has a deep blue color due to the presence of methane in its atmosphere. The methane absorbs red light, causing the planet to appear blue, while the water ice clouds create the white clouds that we see.
Conclusion
The solar system planets are a diverse range of worlds, each with its own unique colors and characteristics. From the scorched grey of Mercury to the deep blue of Neptune, each planet’s color is a result of its distinct composition and atmosphere. By exploring these colors, we can gain a deeper understanding of the planets and their place in our solar system.
What is the most distinctive color of the solar system planets?

+
The most distinctive color of the solar system planets is the red color of Mars, which is caused by the iron oxide particles present in the planet’s soil and rocks.
Which planet has the most striking banded appearance?
+
Jupiter has the most striking banded appearance, which is caused by the presence of different cloud layers in its atmosphere.
What is the primary composition of the solar system planets’ atmospheres?

+
The primary composition of the solar system planets’ atmospheres is hydrogen and helium, with the exception of the rocky planets, which have atmospheres composed of other gases, such as nitrogen and oxygen.



