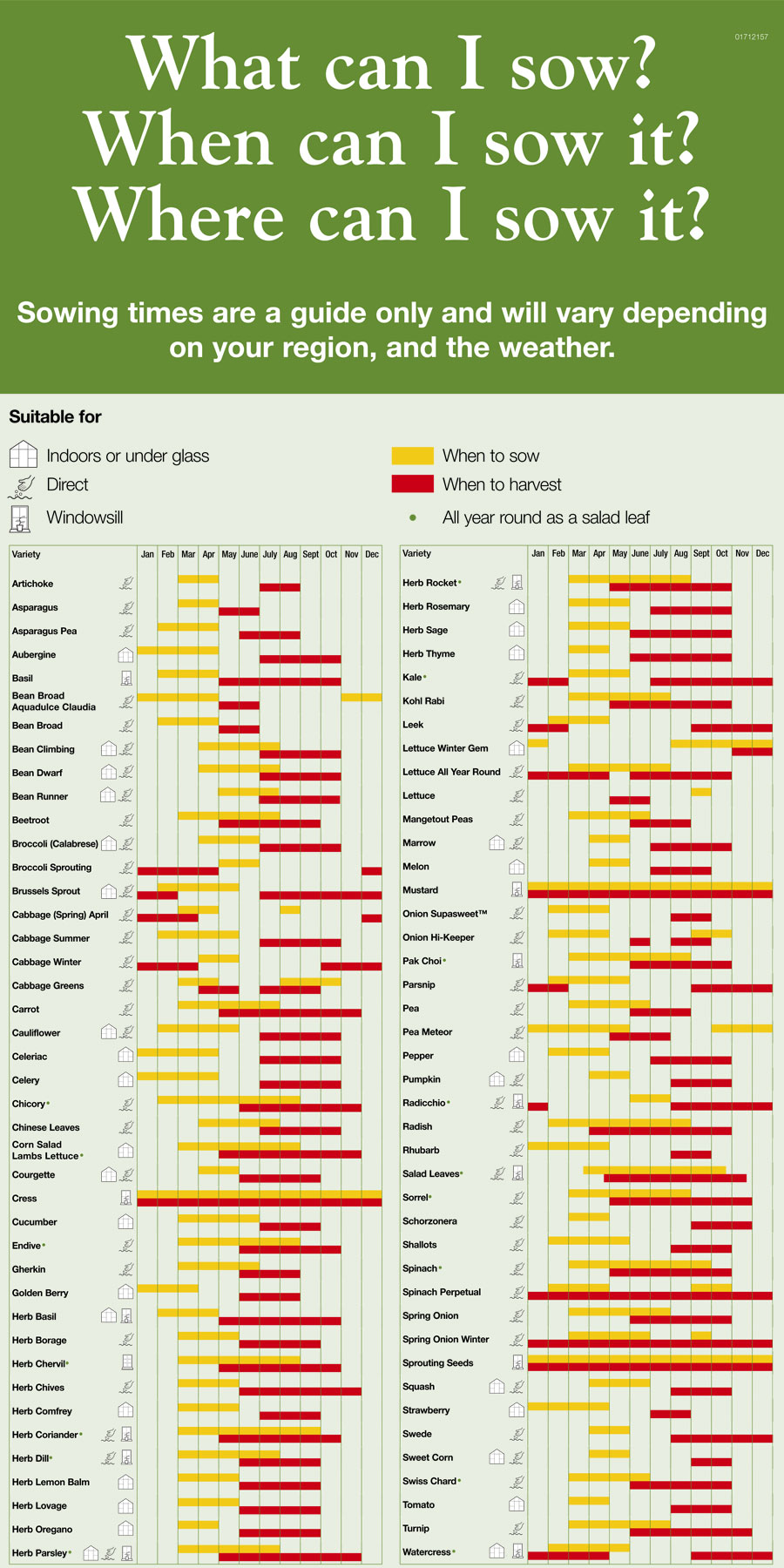
Sow Seeds and Watch Your Garden Grow

Understanding the Basics of Gardening

Gardening is a rewarding hobby that can bring joy and serenity to one’s life. It’s a great way to connect with nature and enjoy the fruits of your labor. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, understanding the basics of gardening is essential for success. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental principles of gardening, from preparing the soil to harvesting your crops.
Preparing the Soil
Before you can start planting, you need to prepare the soil. This involves testing the pH level, removing debris, and adding organic matter. Soil pH is a critical factor in gardening, as it affects the availability of nutrients for your plants. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH, between 6.0 and 7.0.
To test your soil pH, you can purchase a soil testing kit or send a sample to a laboratory for analysis. Once you know your soil pH, you can adjust it by adding lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it.
Adding Organic Matter

Adding organic matter such as compost or manure can improve soil structure, fertility, and overall health. Compost is a rich source of nutrients and can help to neutralize soil pH. You can make your own compost by collecting kitchen scraps, leaves, and grass clippings in a designated bin.
| Soil pH | Soil Type | Plant Preferences |
|---|---|---|
| Acidic (pH 6.0 and below) | Soil with high acidity | Azaleas, blueberries, and rhododendrons |
| Neutral (pH 6.0-7.0) | Soil with balanced pH | Most vegetables, fruits, and flowers |
| Alkaline (pH 7.0 and above) | Soil with high alkalinity | Cacti, succulents, and asparagus |

Choosing the Right Plants

With your soil prepared, it’s time to choose the right plants for your garden. Consider factors such as climate, sunlight, and moisture levels when selecting plants. Annuals are plants that complete their life cycle within a year, while perennials come back year after year.
Some popular annuals include:
- Tomatoes
- Peppers
- Cucumbers
- Carrots
- Radishes
Some popular perennials include:
- Roses
- Daylilies
- Hostas
- Hydrangeas
- Lavender
Companion Planting

Companion planting is the practice of growing different plants together to improve growth, flavor, and pest resistance. For example, planting marigolds with tomatoes can deter nematodes, while basil and mint can improve the flavor of nearby vegetables.
🌼 Note: Companion planting can be a fun and creative way to experiment with different plant combinations. However, some plants may not be compatible, so be sure to research before planting.
Watering and Mulching

Proper watering and mulching are essential for healthy plant growth. Drip irrigation is a efficient way to deliver water directly to the roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. Mulching can help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
Some popular mulching materials include:
- Wood chips
- Straw
- Grass clippings
- Pine needles
- Compost
Common Gardening Mistakes

Avoid common gardening mistakes by:
- Overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other problems
- Underwatering, which can cause stress and reduce growth
- Not providing enough sunlight or shade
- Not fertilizing regularly
- Not pruning or training plants properly
🌱 Note: Gardening is a learning process, and mistakes are inevitable. The key is to observe, adjust, and learn from your mistakes.
As you watch your garden grow, remember to enjoy the process and have fun. Gardening is a journey, not a destination.
Gardening is a rewarding hobby that can bring joy and serenity to one’s life. By understanding the basics of gardening, from preparing the soil to harvesting your crops, you can create a thriving and beautiful garden that will provide you with fresh produce and a sense of accomplishment.
What is the ideal soil pH for most plants?

+
Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH, between 6.0 and 7.0.
What is companion planting?

+
Companion planting is the practice of growing different plants together to improve growth, flavor, and pest resistance.
What is the difference between annuals and perennials?

+
Annuals are plants that complete their life cycle within a year, while perennials come back year after year.