5 Ways Speed of Light is Measured in Mach

Understanding the Speed of Light in Mach

The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics, denoted by the letter c. It is approximately equal to 299,792 kilometers per second (km/s) or 186,282 miles per second (mi/s). Measuring the speed of light is a complex task that has been accomplished through various methods over the years. In this article, we will explore five ways the speed of light is measured in Mach, which is a unit of measurement representing the ratio of an object’s speed to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium.
1. Ole Rømer's Method (1676)

The Danish astronomer Ole Rømer was the first to attempt to measure the speed of light. He observed the eclipses of Jupiter’s moons and noted that the timing of these events varied depending on the Earth’s position relative to Jupiter. By analyzing these observations, Rømer estimated the speed of light to be approximately 220,000 km/s, which is about 26% lower than the actual value. This method was groundbreaking at the time and paved the way for more accurate measurements in the future.
2. Hippolyte Fizeau's Method (1862)

French physicist Hippolyte Fizeau used a rotating wheel to measure the speed of light. He directed a beam of light through the wheel and measured the time it took for the light to pass through the wheel’s teeth. By calculating the time difference between the light passing through the wheel and the wheel’s rotation speed, Fizeau estimated the speed of light to be approximately 298,000 km/s, which is remarkably close to the actual value.
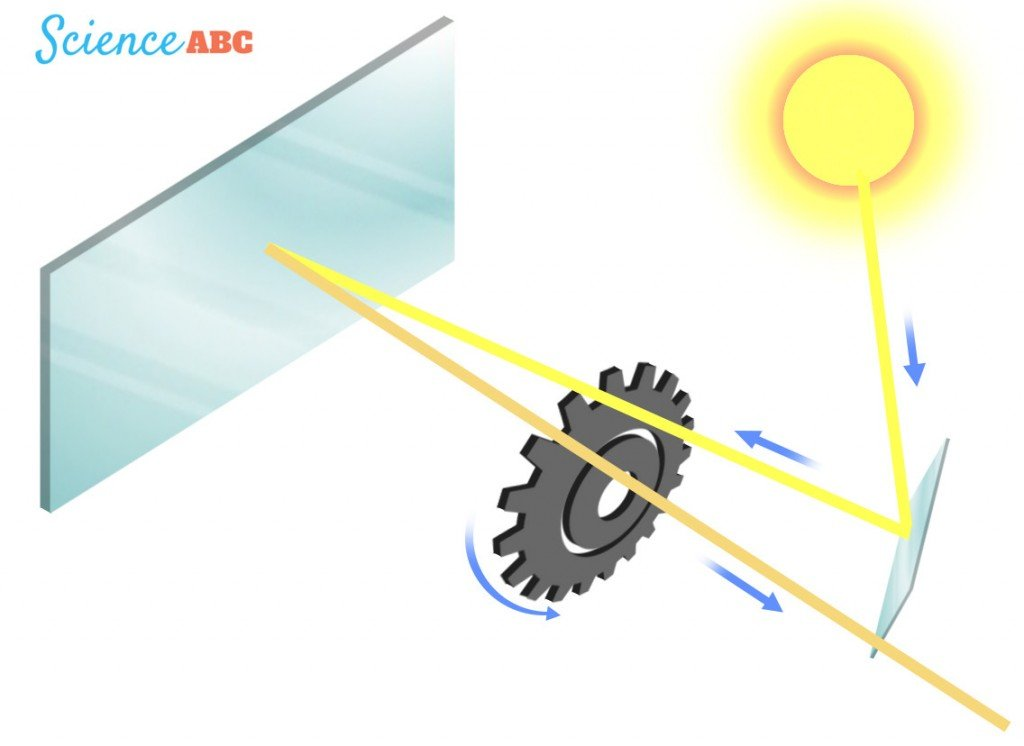
3. Leon Foucault's Method (1862)

Leon Foucault, a French physicist, improved upon Fizeau’s method by using a rotating mirror instead of a wheel. He directed a beam of light at the mirror and measured the time it took for the light to return after reflecting off the mirror. By calculating the time difference between the light’s departure and return, Foucault estimated the speed of light to be approximately 299,796 km/s, which is extremely close to the actual value.
4. Michelson-Morley Experiment (1887)

The Michelson-Morley experiment, conducted by American physicists Albert Michelson and Edward Morley, aimed to measure the speed of light in different directions. They used an interferometer to split a beam of light into two perpendicular paths and measured the time difference between the two paths. The experiment revealed that the speed of light is constant in all directions, which led to the development of Albert Einstein’s theory of special relativity.
5. Laser Interferometry (Modern Method)
Modern methods of measuring the speed of light involve using laser interferometry. This technique involves splitting a laser beam into two paths and measuring the interference patterns created by the recombining beams. By analyzing the interference patterns, scientists can calculate the speed of light with extremely high accuracy. This method has been used to measure the speed of light in various mediums, including air, water, and vacuum.
Conversion to Mach
To express the speed of light in Mach, we need to divide the speed of light by the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. The speed of sound in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure is approximately 343 meters per second (m/s). Therefore, the speed of light in Mach can be calculated as follows:
c (speed of light) = 299,792 km/s ≈ 1,079,252,848.8 Mach (in air)
Note that the speed of light is a fundamental constant and does not change, whereas the speed of sound varies depending on the medium.
📝 Note: The speed of light is a universal constant and does not change, whereas the speed of sound varies depending on the medium.
In conclusion, the speed of light has been measured through various methods over the years, from Ole Rømer’s observations of Jupiter’s moons to modern laser interferometry techniques. Understanding the speed of light is crucial in many fields, including physics, engineering, and astronomy. By expressing the speed of light in Mach, we can appreciate its incredible magnitude and importance in our universe.
What is the speed of light in kilometers per second?

+
The speed of light is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (km/s).
How is the speed of light measured using laser interferometry?

+
Laser interferometry involves splitting a laser beam into two paths and measuring the interference patterns created by the recombining beams. By analyzing the interference patterns, scientists can calculate the speed of light with extremely high accuracy.
What is the speed of sound in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure?

+
The speed of sound in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure is approximately 343 meters per second (m/s).



