Statin Nation: How Cholesterol Drugs Affect National Health Accounts

Understanding the Impact of Statins on National Health Accounts
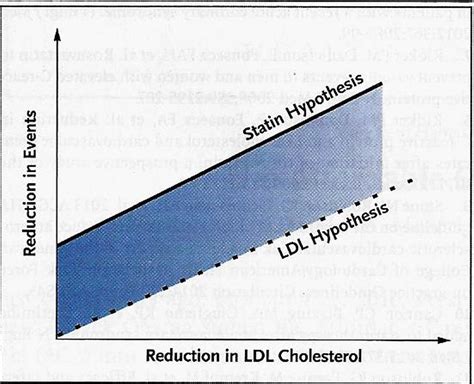
The widespread use of statins, a class of cholesterol-lowering drugs, has significant implications for national health accounts. As one of the most commonly prescribed medications globally, statins have been hailed as a crucial tool in the fight against cardiovascular disease. However, their impact on healthcare systems and economies is multifaceted and warrants closer examination. In this article, we will delve into the effects of statins on national health accounts, exploring both the benefits and drawbacks of these medications.
What are Statins and How Do They Work?
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, work by blocking the enzyme responsible for producing cholesterol in the liver. By reducing the amount of cholesterol produced in the liver, statins lower the overall level of cholesterol in the blood. This, in turn, decreases the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
The Benefits of Statins on National Health Accounts

The use of statins has several benefits for national health accounts:
- Reduced Cardiovascular Disease-Related Costs: By lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease, statins can reduce the economic burden of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events on healthcare systems. A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology estimated that the use of statins could save the United States healthcare system up to $44 billion annually.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Statins have been shown to reduce the risk of major vascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, by up to 30%. This can lead to improved health outcomes, reduced morbidity, and increased productivity.
- Increased Life Expectancy: By reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, statins can increase life expectancy and improve overall quality of life.
The Drawbacks of Statins on National Health Accounts

While statins have several benefits, there are also drawbacks to consider:
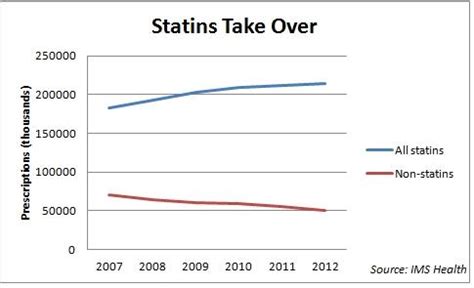
- High Prescription Costs: Statins are among the most commonly prescribed medications globally, and their costs can be substantial. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Lipidology estimated that the annual cost of statin prescriptions in the United States was over $14 billion.
- Side Effects and Adverse Events: Statins can cause side effects, such as muscle pain, liver damage, and cognitive impairment, which can lead to increased healthcare costs and reduced quality of life.
- Overuse and Misuse: Statins are often prescribed to individuals who do not meet the clinical criteria for treatment, leading to unnecessary costs and potential harm.
The Impact of Statins on Healthcare Systems
The use of statins has significant implications for healthcare systems:
- Increased Healthcare Utilization: The use of statins can lead to increased healthcare utilization, including doctor visits, laboratory tests, and hospitalizations.
- Polypharmacy: Statins are often prescribed in combination with other medications, which can increase the risk of polypharmacy and adverse events.
- Healthcare Disparities: The use of statins can exacerbate existing healthcare disparities, particularly in low-income and minority populations, who may have limited access to healthcare services.
Conclusion

The impact of statins on national health accounts is complex and multifaceted. While statins have several benefits, including reduced cardiovascular disease-related costs and improved health outcomes, there are also drawbacks to consider, such as high prescription costs, side effects, and overuse. To maximize the benefits of statins while minimizing their drawbacks, healthcare systems must implement evidence-based guidelines, monitor prescription patterns, and address existing healthcare disparities.
What are the benefits of statins on national health accounts?

+
The benefits of statins on national health accounts include reduced cardiovascular disease-related costs, improved health outcomes, and increased life expectancy.
What are the drawbacks of statins on national health accounts?
+
The drawbacks of statins on national health accounts include high prescription costs, side effects, and overuse.
How can healthcare systems maximize the benefits of statins while minimizing their drawbacks?

+
Healthcare systems can maximize the benefits of statins while minimizing their drawbacks by implementing evidence-based guidelines, monitoring prescription patterns, and addressing existing healthcare disparities.



