Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum Wavelength Revealed

Understanding Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum
Sulfuric acid, a widely used chemical compound, has been extensively studied for its various applications and properties. One crucial aspect of sulfuric acid is its absorption spectrum, which reveals vital information about its molecular structure and behavior. In this article, we will delve into the sulfuric acid absorption spectrum, focusing on the wavelength and its significance.
The Importance of Absorption Spectrum
The absorption spectrum is a graphical representation of the absorption of light by a molecule as a function of wavelength. This spectrum provides valuable information about the molecular structure, electronic transitions, and vibrational modes of a compound. By analyzing the absorption spectrum, scientists can gain insights into the properties and behavior of sulfuric acid.
Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum Wavelength
Studies have shown that sulfuric acid exhibits a characteristic absorption spectrum with distinct peaks and valleys. The absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid typically ranges from 200 to 400 nanometers (nm), with prominent peaks at around 210, 240, and 290 nm. These peaks correspond to specific electronic transitions within the molecule.
Peak 1: 210 nm
The peak at 210 nm is attributed to the n-σ* transition, which involves the promotion of an electron from a non-bonding orbital to a σ* orbital. This transition is associated with the sulfur-oxygen bond.
Peak 2: 240 nm
The peak at 240 nm is due to the π-π* transition, which involves the promotion of an electron from a π orbital to a π* orbital. This transition is associated with the double bonds in the sulfuric acid molecule.
Peak 3: 290 nm
The peak at 290 nm is attributed to the n-π* transition, which involves the promotion of an electron from a non-bonding orbital to a π* orbital. This transition is also associated with the sulfur-oxygen bond.
Significance of Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum

The absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid is essential in various fields, including chemistry, environmental science, and industrial applications. Some of the significant implications of the sulfuric acid absorption spectrum include:
- Environmental monitoring: The absorption spectrum can be used to detect and quantify sulfuric acid in environmental samples, such as water and air.
- Industrial applications: The absorption spectrum is crucial in monitoring the quality and concentration of sulfuric acid in industrial processes, such as fertilizer production and petroleum refining.
- Chemical research: The absorption spectrum provides valuable information about the molecular structure and electronic transitions of sulfuric acid, which is essential for understanding its chemical properties and behavior.
🔍 Note: The absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid can be affected by various factors, such as temperature, concentration, and solvent effects. Therefore, it is essential to consider these factors when interpreting the absorption spectrum.
Conclusion
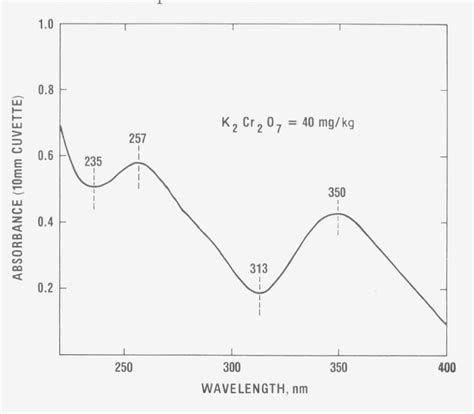
In conclusion, the sulfuric acid absorption spectrum wavelength reveals vital information about the molecular structure and electronic transitions of sulfuric acid. The characteristic peaks at 210, 240, and 290 nm provide insights into the properties and behavior of sulfuric acid, making it an essential tool in various fields.
What is the significance of the absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid?
+
The absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid is essential in various fields, including chemistry, environmental science, and industrial applications. It provides valuable information about the molecular structure and electronic transitions of sulfuric acid.
What are the characteristic peaks in the absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid?
+
The characteristic peaks in the absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid are at 210, 240, and 290 nm. These peaks correspond to specific electronic transitions within the molecule.
How can the absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid be affected?
+
The absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid can be affected by various factors, such as temperature, concentration, and solvent effects. Therefore, it is essential to consider these factors when interpreting the absorption spectrum.



