5 Ways to Read a Topographic Map of Texas
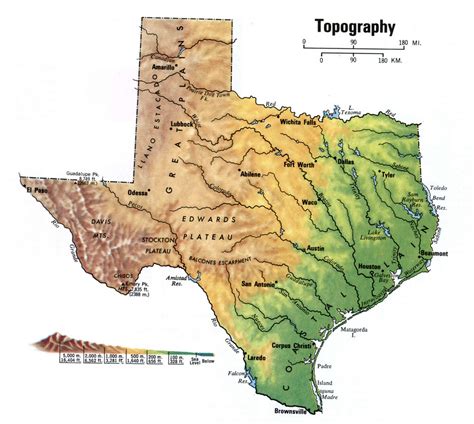
Understanding Topographic Maps
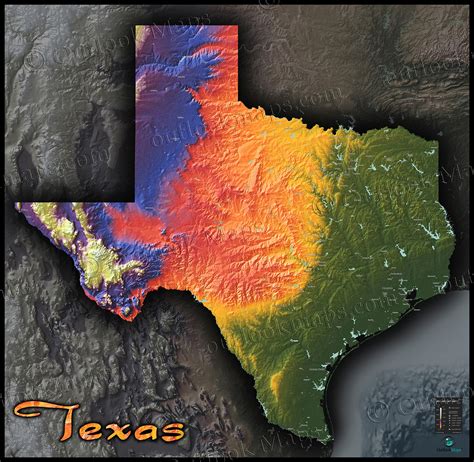
When exploring the vast and diverse landscapes of Texas, a topographic map is an essential tool for any outdoors enthusiast, hiker, or researcher. Topographic maps provide a detailed representation of the terrain, including elevation, water bodies, and vegetation. However, deciphering the various symbols, colors, and markings on a topographic map can be overwhelming for those new to map reading. In this article, we will guide you through the process of reading a topographic map of Texas, highlighting five key aspects to get you started.
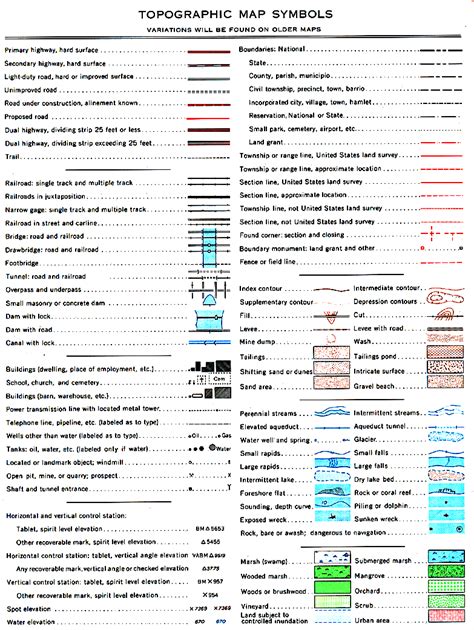
1. Understanding Map Symbols and Colors
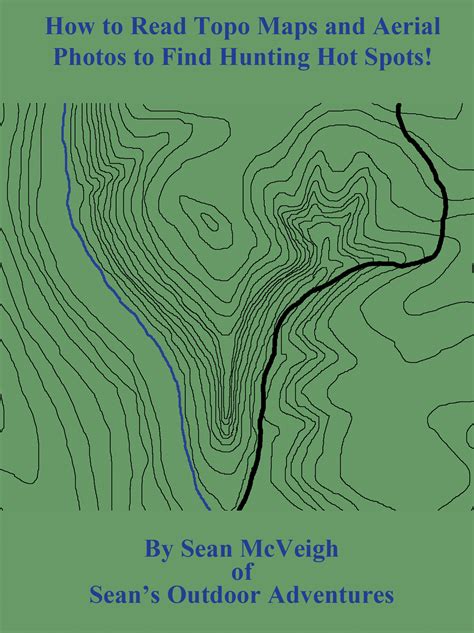
Topographic maps use a variety of symbols and colors to represent different features of the terrain. Familiarize yourself with the legend, usually located in a corner of the map, which explains the meaning of each symbol and color. Some common symbols include:
- Contours: Brown lines that indicate elevation, with each line representing a specific elevation interval (usually 20 or 40 feet).
- Water bodies: Blue lines and shapes representing rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
- Vegetation: Green areas indicating forests, grasslands, or other types of vegetation.
- Man-made features: Black lines and shapes representing roads, buildings, and other human-made structures.
🗺️ Note: Pay attention to the scale of the map, which indicates the relationship between distances on the map and real-world distances.
2. Reading Contours and Elevation
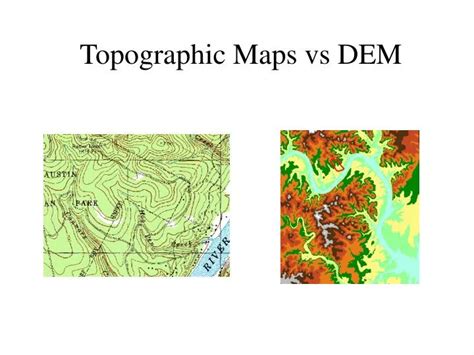
Contours are a crucial aspect of topographic maps, as they provide information about the terrain’s elevation and shape. To read contours effectively:
- Index contours: Identify the thick, dark brown lines that mark every fifth contour interval (usually 100 feet). These lines are labeled with their elevation value.
- Intermediate contours: Look for the lighter brown lines between index contours, which represent the intervening elevation intervals.
- Contour intervals: Note the contour interval, which indicates the elevation difference between consecutive contours.
By analyzing contours, you can determine the shape and elevation of the terrain, including hills, valleys, and ridges.
3. Identifying Water Bodies and Hydrological Features

Water bodies and hydrological features are essential components of a topographic map. To identify these features:
- Rivers and streams: Look for blue lines that flow into larger bodies of water.
- Lakes and reservoirs: Identify blue shapes or areas representing still water bodies.
- Wetlands: Note green or blue areas with irregular shapes, indicating marshy or swampy terrain.
These features can help you understand the hydrological characteristics of the area, including drainage patterns and water sources.
4. Analyzing Vegetation and Land Use
Topographic maps also provide information about vegetation and land use. To analyze these features:
- Forest areas: Identify green areas with tree symbols, indicating wooded regions.
- Grasslands and agricultural areas: Note green or yellow areas with dashed lines or patterns, representing open spaces or cultivated land.
- Urban areas: Look for black shapes or lines indicating built-up areas, such as cities or towns.
By understanding the vegetation and land use patterns, you can gain insights into the ecosystem, climate, and human activities in the area.
5. Using Map Coordinates and Scale
To navigate and locate specific features on a topographic map, it’s essential to understand the map’s coordinates and scale. To use map coordinates:
- Latitude and longitude: Identify the grid system of latitude and longitude lines, which help you pinpoint specific locations.
- Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinates: Note the UTM grid, which provides a more precise way of locating features using easting and northing values.
By combining your understanding of map symbols, contours, water bodies, vegetation, and coordinates, you’ll be able to read a topographic map of Texas with confidence and unlock the secrets of the Lone Star State’s diverse landscapes.
With these five key aspects, you’re ready to start exploring the world of topographic maps and discovering the hidden treasures of Texas’s terrain. Whether you’re a seasoned cartographer or an outdoor enthusiast, the ability to read a topographic map will enhance your appreciation and understanding of the natural world.
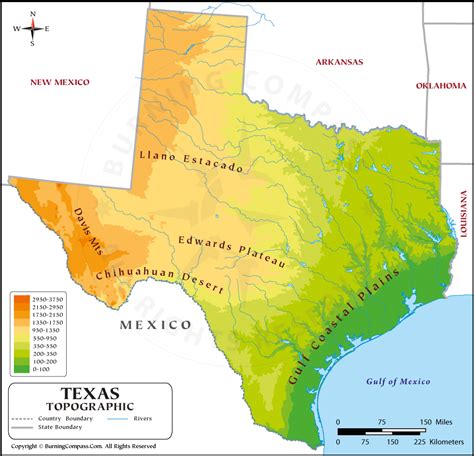
What is the purpose of a topographic map?
+
A topographic map is designed to represent the Earth’s surface features, including elevation, water bodies, and vegetation, providing a detailed and accurate representation of the terrain.
How do I read contour lines on a topographic map?
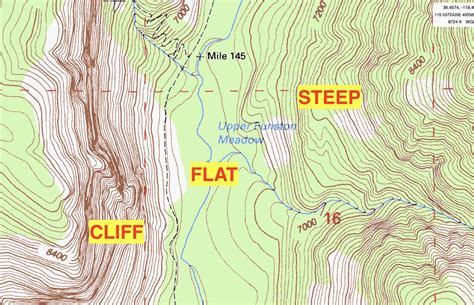
+
Contour lines on a topographic map indicate elevation, with each line representing a specific elevation interval. Index contours are labeled with their elevation value, while intermediate contours represent the intervening elevation intervals.
What do the different colors on a topographic map represent?

+
Colors on a topographic map represent different features, including brown for contours, blue for water bodies, green for vegetation, and black for man-made features. The legend explains the meaning of each color and symbol.