US Army Branches List: Exploring the Different Divisions

Understanding the US Army Branches

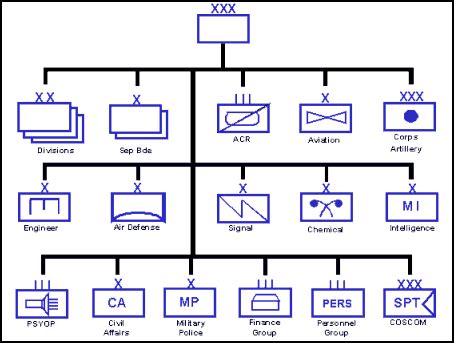
The US Army is one of the largest and most complex military organizations in the world, comprising numerous branches that work together to ensure the defense of the United States. The various branches of the US Army are responsible for different functions, from combat and engineering to intelligence and communications. In this article, we will explore the different divisions within the US Army, their roles, and responsibilities.
Infantry Branch

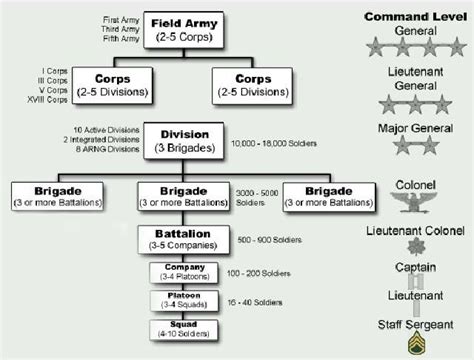
The Infantry Branch is one of the largest and most recognizable branches of the US Army. Infantry soldiers are trained to engage in combat and are responsible for the defense of the country. The Infantry Branch is divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Rifle and Machine Gun Units: These units are responsible for conducting ground combat operations and providing security for other units.
- Reconnaissance Units: These units conduct reconnaissance and surveillance missions to gather intelligence on enemy positions and movements.
- Airborne and Air Assault Units: These units are trained to conduct airborne and air assault operations, using aircraft to transport troops and equipment into combat zones.
🔍 Note: Infantry soldiers are known for their bravery and sacrifice, and are often the first line of defense in combat situations.
Armor Branch

The Armor Branch is responsible for the operation and maintenance of armored vehicles, such as tanks and armored personnel carriers. Armor soldiers are trained to conduct combat operations and provide security for other units.
- Tank Units: These units operate and maintain tanks, which are used to provide firepower and protection for infantry units.
- Armored Cavalry Units: These units operate and maintain armored personnel carriers, which are used to transport troops and equipment in combat zones.
Artillery Branch

The Artillery Branch is responsible for providing indirect fire support to infantry and armor units. Artillery soldiers are trained to operate and maintain artillery systems, such as howitzers and mortars.
- Field Artillery Units: These units provide indirect fire support to infantry and armor units, using howitzers and other artillery systems.
- Air Defense Artillery Units: These units provide air defense for ground units, using surface-to-air missile systems and other air defense systems.
Engineer Branch

The Engineer Branch is responsible for providing engineering support to other units, including the construction and repair of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. Engineer soldiers are trained to operate and maintain engineering equipment, such as bulldozers and cranes.
- Combat Engineer Units: These units provide engineering support to infantry and armor units, including the construction and repair of roads and bridges.
- Construction Engineer Units: These units provide engineering support for the construction of infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings.
Signal Branch

The Signal Branch is responsible for providing communications support to other units, including the installation and maintenance of communications systems. Signal soldiers are trained to operate and maintain communications equipment, such as radios and satellite systems.
- Network Operations Units: These units provide network operations support to other units, including the installation and maintenance of communications systems.
- Communications Security Units: These units provide communications security support to other units, including the encryption and decryption of messages.
Intelligence Branch

The Intelligence Branch is responsible for providing intelligence support to other units, including the collection and analysis of intelligence data. Intelligence soldiers are trained to operate and maintain intelligence systems, such as surveillance and reconnaissance systems.
- Human Intelligence Units: These units collect and analyze human intelligence data, including information gathered from sources and interrogations.
- Signals Intelligence Units: These units collect and analyze signals intelligence data, including information gathered from communications systems.
Other Branches

In addition to the branches listed above, the US Army also includes several other branches, including:
- Adjutant General Branch: This branch is responsible for providing personnel support to other units, including the management of personnel records and the administration of personnel policies.
- Chaplain Branch: This branch is responsible for providing spiritual support to soldiers, including the provision of chaplain services and the administration of religious programs.
- Judge Advocate General Branch: This branch is responsible for providing legal support to other units, including the administration of military justice and the provision of legal advice.
Conclusion
The US Army is a complex and diverse organization, comprising numerous branches that work together to ensure the defense of the United States. Each branch has its own unique role and responsibilities, and soldiers who serve in these branches are trained to perform a variety of tasks and functions. By understanding the different branches of the US Army, we can gain a better appreciation for the sacrifices and contributions of the men and women who serve in our military.
What is the largest branch of the US Army?
+
The largest branch of the US Army is the Infantry Branch, which is responsible for conducting ground combat operations and providing security for other units.
What is the role of the Engineer Branch?

+
The Engineer Branch is responsible for providing engineering support to other units, including the construction and repair of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure.
What is the role of the Intelligence Branch?

+
The Intelligence Branch is responsible for providing intelligence support to other units, including the collection and analysis of intelligence data.