US Marine Officer Ranks Explained

Understanding the US Marine Officer Ranks

The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the US Armed Forces with a rich history and a reputation for excellence. The Marine Corps officer ranks are a crucial part of the organization’s structure and hierarchy. In this article, we will delve into the different officer ranks in the US Marine Corps, their responsibilities, and the requirements for advancement.
Commissioned Officer Ranks
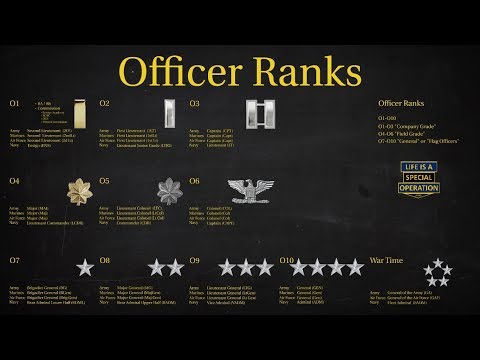
Commissioned officers in the US Marine Corps are leaders who have completed a four-year college degree and the Officer Candidates School (OCS) or the United States Naval Academy. They hold positions of authority and are responsible for making key decisions.
Second Lieutenant (2ndLt)

- O-1
- The entry-level rank for commissioned officers
- Typically serves as a platoon leader or executive officer
- Responsible for leading and training a small unit of Marines
First Lieutenant (1stLt)

- O-2
- Typically serves as a company executive officer or a platoon commander
- Responsible for leading and training a larger unit of Marines
- Begins to take on more responsibilities and develop leadership skills
Captain (Capt)

- O-3
- Typically serves as a company commander or a battalion staff officer
- Responsible for leading and training a company-sized unit of Marines
- Develops advanced leadership and management skills
Major (Maj)

- O-4
- Typically serves as a battalion executive officer or a regimental staff officer
- Responsible for leading and training a battalion-sized unit of Marines
- Develops strategic leadership and planning skills
Field Grade Officer Ranks

Field grade officers are experienced leaders who have demonstrated exceptional skills and dedication. They hold positions of significant responsibility and are responsible for making critical decisions.
Lieutenant Colonel (LtCol)

- O-5
- Typically serves as a battalion commander or a regimental staff officer
- Responsible for leading and training a battalion-sized unit of Marines
- Develops advanced strategic leadership and planning skills
Colonel (Col)

- O-6
- Typically serves as a regimental commander or a division staff officer
- Responsible for leading and training a regiment-sized unit of Marines
- Develops senior leadership and management skills
General Officer Ranks

General officers are the highest-ranking leaders in the US Marine Corps. They hold positions of significant authority and are responsible for making key decisions that impact the entire organization.
Brigadier General (BGen)

- O-7
- Typically serves as a deputy commanding general or a division staff officer
- Responsible for leading and training a division-sized unit of Marines
- Develops advanced senior leadership and management skills
Major General (MajGen)

- O-8
- Typically serves as a commanding general or a joint task force commander
- Responsible for leading and training a major command-sized unit of Marines
- Develops exceptional senior leadership and management skills
Lieutenant General (LtGen)

- O-9
- Typically serves as a deputy commandant or a joint task force commander
- Responsible for leading and training a major command-sized unit of Marines
- Develops advanced exceptional senior leadership and management skills
General (Gen)

- O-10
- The highest-ranking officer in the US Marine Corps
- Typically serves as the commandant of the Marine Corps
- Responsible for leading and training the entire organization
📝 Note: Officer ranks and responsibilities may vary depending on the specific job and location.
Warrant Officer Ranks

Warrant officers are technical experts who have demonstrated exceptional skills and knowledge in a specific area. They hold positions of significant responsibility and are responsible for providing guidance and advice.
Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)
- W-1
- The entry-level rank for warrant officers
- Typically serves as a technical expert in a specific area
- Responsible for providing guidance and advice to junior Marines
Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CWO2)
- W-2
- Typically serves as a senior technical expert in a specific area
- Responsible for providing guidance and advice to junior Marines
- Begins to take on more responsibilities and develop leadership skills
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CWO3)
- W-3
- Typically serves as a senior technical expert in a specific area
- Responsible for providing guidance and advice to junior Marines
- Develops advanced leadership and management skills
Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CWO4)
- W-4
- Typically serves as a senior technical expert in a specific area
- Responsible for providing guidance and advice to junior Marines
- Develops exceptional leadership and management skills
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CWO5)
- W-5
- The highest-ranking warrant officer in the US Marine Corps
- Typically serves as a senior technical expert in a specific area
- Responsible for providing guidance and advice to junior Marines
Enlisted Ranks

Enlisted Marines are the backbone of the organization. They hold positions of significant responsibility and are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations of the Marine Corps.
We will not go into details about the enlisted ranks in this article.
Conclusion

The US Marine Corps officer ranks are a crucial part of the organization’s structure and hierarchy. From second lieutenant to general, each rank has its own unique responsibilities and requirements. Understanding these ranks and their responsibilities can help individuals navigate the organization and achieve their goals.
What is the highest rank in the US Marine Corps?
+The highest rank in the US Marine Corps is General (O-10).
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?
+A commissioned officer is a leader who has completed a four-year college degree and the Officer Candidates School (OCS) or the United States Naval Academy. A warrant officer is a technical expert who has demonstrated exceptional skills and knowledge in a specific area.
How do I become an officer in the US Marine Corps?
+To become an officer in the US Marine Corps, you must complete a four-year college degree and the Officer Candidates School (OCS) or the United States Naval Academy.



