9 Military Enlisted Ranks You Need to Know

Understanding the Hierarchy: 9 Military Enlisted Ranks You Need to Know
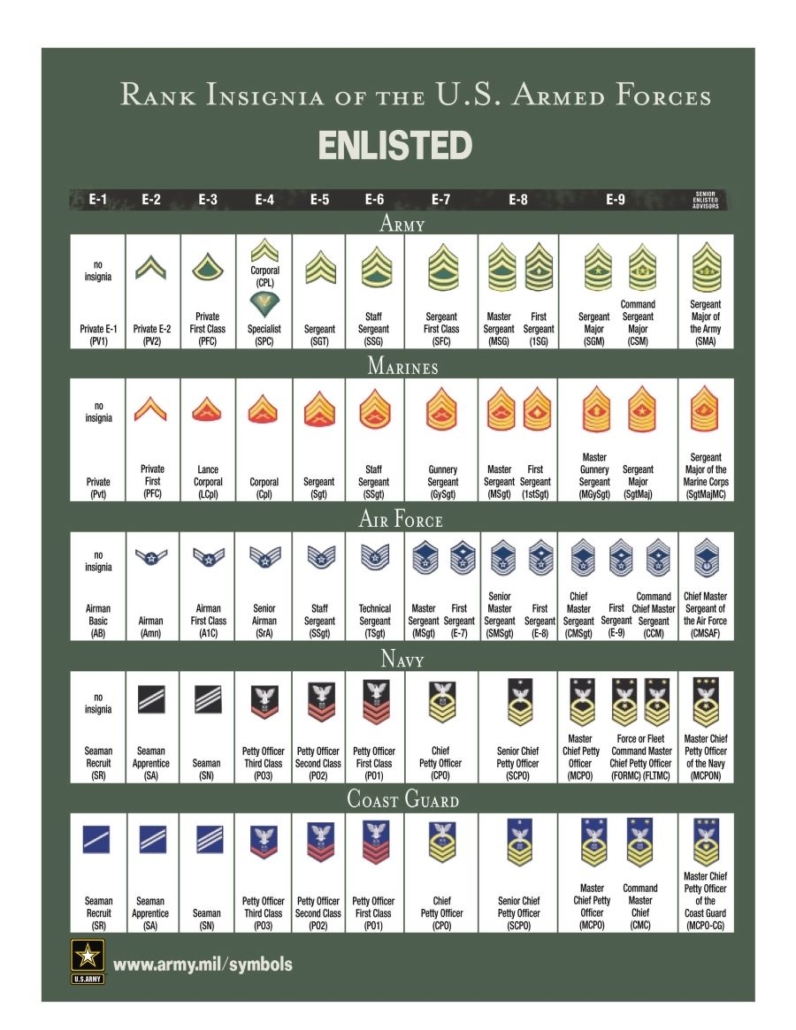
Joining the military can be a life-changing decision, and understanding the rank structure is essential for anyone considering a career in the armed forces. The enlisted ranks are the backbone of the military, making up the majority of the personnel. In this article, we’ll break down the 9 military enlisted ranks, from the lowest to the highest, and provide an overview of the roles and responsibilities associated with each rank.
The Entry-Level Ranks: E-1 to E-3

The first three ranks are considered entry-level and are typically held by new recruits.
- Private (E-1): The lowest rank in the military, privates are new recruits who are still in basic training. They have no special duties and are still learning the ways of the military.
- Private Second Class (E-2): After completing basic training, privates are promoted to private second class. They may be given additional responsibilities, such as mentoring new recruits.
- Private First Class (E-3): Privates first class have gained some experience and may be given leadership roles, such as leading a team or squad.
The Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks: E-4 to E-6

The next three ranks are considered non-commissioned officer (NCO) ranks, which are leadership positions that require more experience and training.
- Corporal (E-4): Corporals are the first level of NCOs and are responsible for leading teams and squads. They may also be given additional duties, such as training new recruits.
- Sergeant (E-5): Sergeants are experienced NCOs who lead platoons and companies. They are responsible for making tactical decisions and mentoring junior soldiers.
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): Staff sergeants are senior NCOs who lead battalions and brigades. They are responsible for making strategic decisions and advising officers.
The Senior Enlisted Ranks: E-7 to E-9

The final three ranks are considered senior enlisted ranks, which are the highest levels of enlisted leadership.
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): Sergeant first class is a senior enlisted rank that requires a high level of experience and leadership ability. They may lead battalions and brigades and advise officers.
- Master Sergeant (E-8): Master sergeants are senior enlisted leaders who have achieved a high level of expertise in their field. They may lead divisions and corps and advise general officers.
- Sergeant Major (E-9): Sergeant major is the highest enlisted rank in the military. They are senior leaders who have achieved a high level of experience and expertise. They may advise general officers and lead entire branches of the military.
💡 Note: The ranks and responsibilities may vary depending on the branch of service and the country's military structure.
| Rank | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Private | PVT | Entry-level rank, still in basic training |
| Private Second Class | PV2 | Entry-level rank, completed basic training |
| Private First Class | PFC | Entry-level rank, gained some experience |
| Corporal | CPL | First level of NCO, leads teams and squads |
| Sergeant | SGT | Experienced NCO, leads platoons and companies |
| Staff Sergeant | SSG | Senior NCO, leads battalions and brigades |
| Sergeant First Class | SFC | Senior enlisted rank, leads battalions and brigades |
| Master Sergeant | MSG | Senior enlisted leader, achieved high level of expertise |
| Sergeant Major | SGM | Highest enlisted rank, senior leader and advisor |

In conclusion, understanding the military enlisted ranks is essential for anyone considering a career in the armed forces. From the entry-level ranks to the senior enlisted ranks, each level requires a different level of experience, training, and leadership ability. By knowing the ranks and responsibilities, individuals can better navigate the military hierarchy and achieve their career goals.
What is the difference between a private and a private first class?

+
A private first class has gained some experience and may be given leadership roles, such as leading a team or squad. A private, on the other hand, is an entry-level rank still in basic training.
What is the role of a sergeant major?

+
A sergeant major is the highest enlisted rank in the military. They are senior leaders who have achieved a high level of experience and expertise, and may advise general officers and lead entire branches of the military.
How do I get promoted to the next rank?

+
Promotions are based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance, and education. Soldiers must meet the requirements for each rank and be recommended for promotion by their superiors.



