What is a W-8BEN-E Form and How to Fill It Out
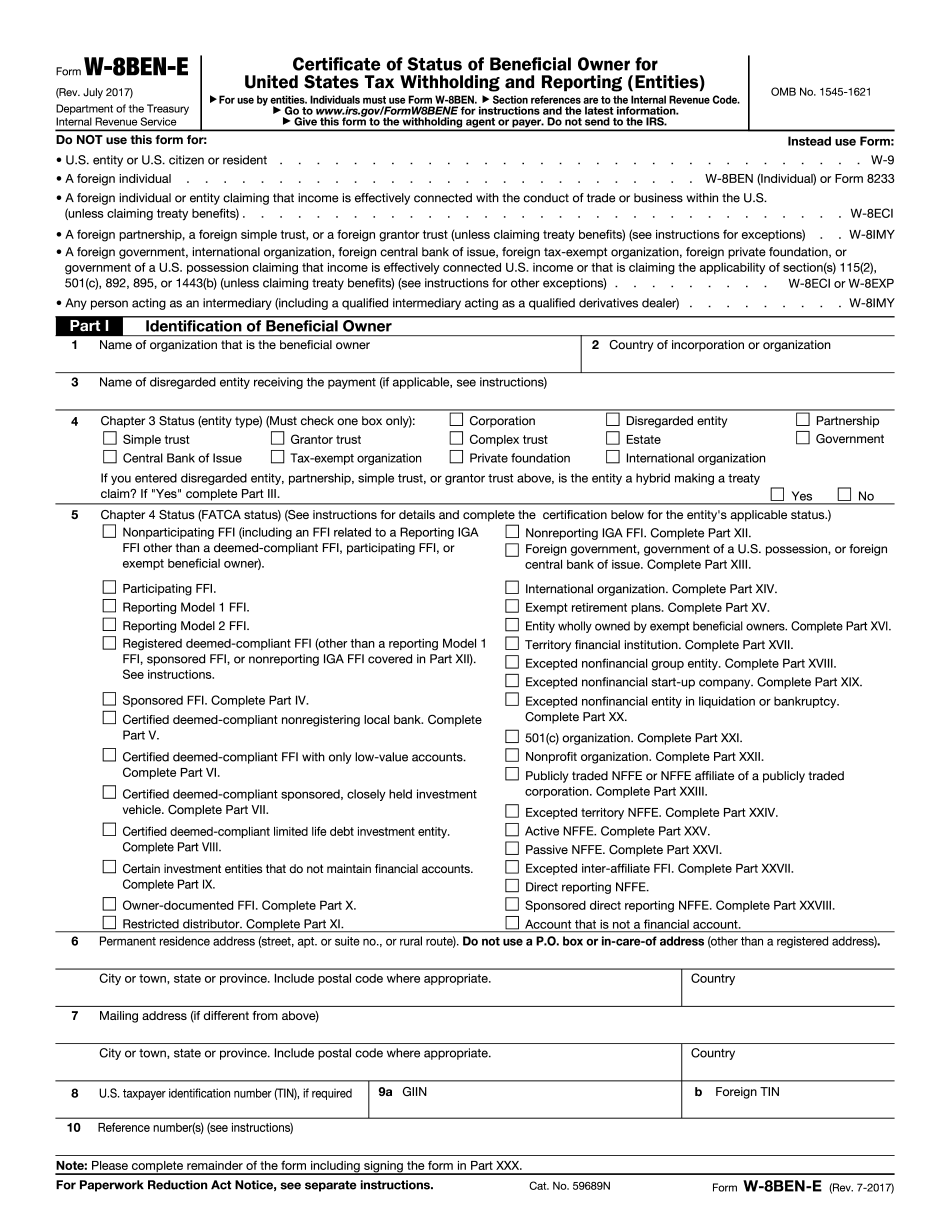
Understanding the W-8BEN-E Form
The W-8BEN-E form is a crucial document for foreign entities that conduct business with the United States. It is used to certify the foreign status of a business entity or individual, allowing them to claim reduced tax rates or exemptions under the US tax laws. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of the W-8BEN-E form, its purpose, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to fill it out.
Purpose of the W-8BEN-E Form

The W-8BEN-E form is used to:
- Certify the foreign status of a business entity or individual
- Claim reduced tax rates or exemptions under the US tax laws
- Provide documentation for the foreign entity’s tax identification number (TIN)
- Identify the entity’s classification for US tax purposes
Who Needs to Fill Out the W-8BEN-E Form?

The following foreign entities need to fill out the W-8BEN-E form:
- Foreign corporations
- Foreign partnerships
- Foreign trusts
- Foreign estates
- Non-resident aliens (individuals)
Step-by-Step Guide to Filling Out the W-8BEN-E Form

The W-8BEN-E form consists of 30 questions, divided into four parts. Here’s a step-by-step guide to filling out the form:
Part I: Identification of Beneficial Owner
- Question 1: Enter the name of the foreign entity or individual.
- Question 2: Provide the foreign entity’s or individual’s country of incorporation or nationality.
- Question 3: Enter the foreign entity’s or individual’s address.
- Question 4: Provide the foreign entity’s or individual’s US taxpayer identification number (if applicable).
Part II: Claim of Tax Treaty Benefits
- Question 5: Check if the foreign entity or individual is claiming tax treaty benefits.
- Question 6: Identify the tax treaty country.
- Question 7: Enter the article and paragraph of the tax treaty that supports the claim.
Part III: Certification
- Question 8: Certify that the foreign entity or individual is not a US person.
- Question 9: Certify that the foreign entity or individual meets the requirements for reduced tax rates or exemptions under the US tax laws.
Part IV: Additional Information
- Question 10-30: Provide additional information, such as the foreign entity’s or individual’s date of birth, address, and tax identification number.
📝 Note: It is essential to carefully review the instructions and provide accurate information when filling out the W-8BEN-E form.
Additional Requirements

In addition to filling out the W-8BEN-E form, foreign entities or individuals may need to provide additional documentation, such as:
- A certificate of incorporation or registration
- A tax identification number (TIN) confirmation letter
- A copy of the tax treaty
📝 Note: The W-8BEN-E form is valid for three years from the date of signing. It is essential to update the form if there are any changes to the foreign entity's or individual's status.
Consequences of Not Filing the W-8BEN-E Form

Failure to file the W-8BEN-E form or providing inaccurate information can result in:
- Tax penalties
- Interest charges
- Loss of tax treaty benefits
- Delayed or denied payments
Conclusion

The W-8BEN-E form is a critical document for foreign entities or individuals conducting business with the United States. It is essential to carefully review the instructions and provide accurate information when filling out the form. Failure to do so can result in tax penalties and loss of tax treaty benefits. By following this step-by-step guide, foreign entities or individuals can ensure compliance with the US tax laws and avoid any potential consequences.
What is the purpose of the W-8BEN-E form?

+
The W-8BEN-E form is used to certify the foreign status of a business entity or individual, allowing them to claim reduced tax rates or exemptions under the US tax laws.
Who needs to fill out the W-8BEN-E form?

+
Foreign corporations, partnerships, trusts, estates, and non-resident aliens (individuals) need to fill out the W-8BEN-E form.
What are the consequences of not filing the W-8BEN-E form?

+
Failure to file the W-8BEN-E form or providing inaccurate information can result in tax penalties, interest charges, loss of tax treaty benefits, and delayed or denied payments.



