7 Key Differences Between Walnuts and Pecans

Navigating the World of Tree Nuts: A Comprehensive Guide

Tree nuts are a delicious and nutritious snack that can add crunch, flavor, and nutrition to various dishes. Among the numerous types of tree nuts, walnuts and pecans stand out for their rich, buttery flavors and versatility in both sweet and savory recipes. While both walnuts and pecans are widely consumed and enjoyed, they exhibit distinct differences in terms of their origin, nutritional content, taste, and uses in cooking. Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices when selecting ingredients for your favorite recipes.
Origin and Cultivation

Walnuts and pecans have different origins and cultivation practices. Walnuts are native to Asia and southeastern Europe, with China being the largest producer. They are primarily grown in temperate climates with mild winters and warm summers. Pecans, on the other hand, are native to North America, specifically the southern United States and Mexico. They thrive in warmer climates with well-drained soil.
Tree Characteristics

Walnut trees are generally larger than pecan trees, with some varieties reaching heights of over 100 feet. Pecan trees are more compact, with an average height of 70-80 feet. Walnut trees also have a broader canopy and a longer lifespan, with some trees living up to 200 years. Pecan trees have a shorter lifespan, typically living between 100-150 years.
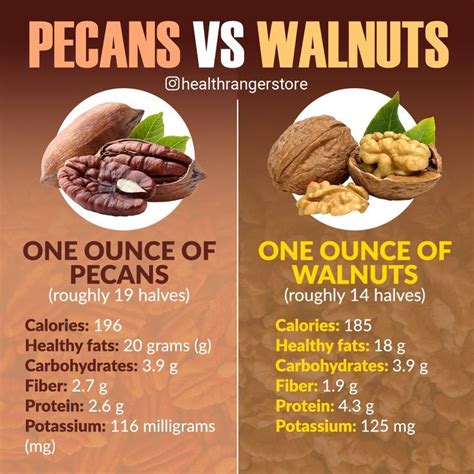
Nutritional Content

Both walnuts and pecans are rich in nutrients, but they differ in their nutritional profiles. Walnuts are higher in:
- Protein: Walnuts contain about 14.7% protein, while pecans have around 7.5%.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Walnuts are a rich source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. Pecans have a lower ALA content.
- Antioxidants: Walnuts have a higher antioxidant capacity due to their high content of polyphenols and phenolic acids.
Pecans, however, are higher in:
- Fat content: Pecans have a higher fat content than walnuts, with about 70% fat compared to walnuts’ 65%.
- Carbohydrates: Pecans contain more carbohydrates than walnuts, including natural sugars and fiber.
- Minerals: Pecans are a good source of minerals like zinc, magnesium, and potassium.
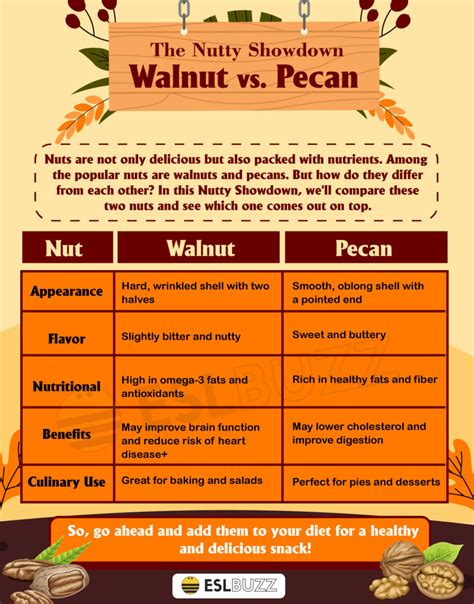
Taste and Texture

The taste and texture of walnuts and pecans are distinct. Walnuts have a:
- Rich, earthy flavor: Walnuts are known for their robust, slightly bitter taste.
- Coarse texture: Walnuts have a rough, crunchy texture due to their high oil content.
Pecans, on the other hand, have a:
- Buttery, sweet flavor: Pecans are famous for their rich, buttery taste and aroma.
- Smooth texture: Pecans are generally smoother and more delicate in texture than walnuts.
Culinary Uses

Both walnuts and pecans are versatile ingredients, but they’re used in different ways:
- Walnuts: Walnuts are often used in baked goods, salads, and savory dishes like stir-fries and curries. They’re also a popular topping for yogurt, oatmeal, and ice cream.
- Pecans: Pecans are commonly used in sweet dishes like pies, cakes, and cookies. They’re also a popular topping for salads, yogurt, and ice cream.
Shelf Life and Storage
Walnuts and pecans have different storage requirements due to their oil content:
- Walnuts: Walnuts are more prone to rancidity due to their high oil content. They should be stored in a cool, dry place or refrigerated to maintain freshness.
- Pecans: Pecans have a lower oil content and can be stored at room temperature for a longer period. However, it’s still recommended to store them in an airtight container to maintain freshness.
Pricing and Availability
The price and availability of walnuts and pecans vary depending on the region and season:
- Walnuts: Walnuts are generally more expensive than pecans, especially high-quality varieties. They’re widely available in most supermarkets and online stores.
- Pecans: Pecans are often cheaper than walnuts, especially in regions where they’re locally grown. They’re widely available in the United States and can be found in most supermarkets.
💡 Note: The prices and availability of walnuts and pecans may vary depending on your location and the time of year.
In conclusion, while both walnuts and pecans are delicious and nutritious, they exhibit distinct differences in terms of their origin, nutritional content, taste, and uses in cooking. By understanding these differences, you can make informed choices when selecting ingredients for your favorite recipes and enjoy the unique benefits of each nut.
What is the main difference between walnuts and pecans?

+
The main difference between walnuts and pecans is their origin, nutritional content, taste, and uses in cooking. Walnuts are native to Asia and have a richer, earthier flavor, while pecans are native to North America and have a buttery, sweet flavor.
Which nut is higher in protein?

+
Walnuts are higher in protein, containing about 14.7% protein compared to pecans’ 7.5%.
Can I substitute walnuts for pecans in recipes?

+
While you can substitute walnuts for pecans in some recipes, keep in mind that they have different flavors and textures. Walnuts have a coarser texture and a richer flavor, while pecans are smoother and have a buttery flavor. Some recipes may require adjustments to accommodate these differences.



