Weave 3D Symmetry Made Easy

Understanding 3D Symmetry: A Comprehensive Guide
Three-dimensional (3D) symmetry is a fundamental concept in various fields, including art, architecture, engineering, and mathematics. It refers to the quality of being unchanged under a particular transformation, such as rotation, reflection, or scaling. In this article, we will delve into the world of 3D symmetry, exploring its types, importance, and applications. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will be well-versed in the concept of 3D symmetry and its significance in various industries.
Types of 3D Symmetry

There are several types of 3D symmetry, each with its unique characteristics and applications:
- Reflection Symmetry: This type of symmetry occurs when an object remains unchanged after being reflected across a plane. For example, a sphere has reflection symmetry because it looks the same when reflected across any plane that passes through its center.
- Rotational Symmetry: Rotational symmetry occurs when an object remains unchanged after being rotated around a central axis. A cube has rotational symmetry because it looks the same after being rotated by 90 degrees around any axis that passes through its center.
- Helical Symmetry: Helical symmetry occurs when an object remains unchanged after being rotated and translated along a helical path. A spiral staircase is an example of an object with helical symmetry.
- Screw Symmetry: Screw symmetry occurs when an object remains unchanged after being rotated and translated along a screw axis. A screw thread is an example of an object with screw symmetry.
Importance of 3D Symmetry

3D symmetry plays a crucial role in various industries, including:
- Art and Architecture: Symmetry is a fundamental element of art and architecture, used to create aesthetically pleasing and balanced compositions. From the symmetry of ancient Greek temples to the intricate patterns of Islamic art, symmetry has been a cornerstone of artistic expression.
- Engineering: Symmetry is essential in engineering, where it is used to design and optimize structures, such as bridges, buildings, and machines. Symmetry helps engineers to ensure that their designs are stable, efficient, and cost-effective.
- Mathematics: Symmetry is a fundamental concept in mathematics, used to describe the properties of geometric shapes and objects. Mathematicians use symmetry to classify and analyze objects, revealing their underlying structure and properties.
Applications of 3D Symmetry
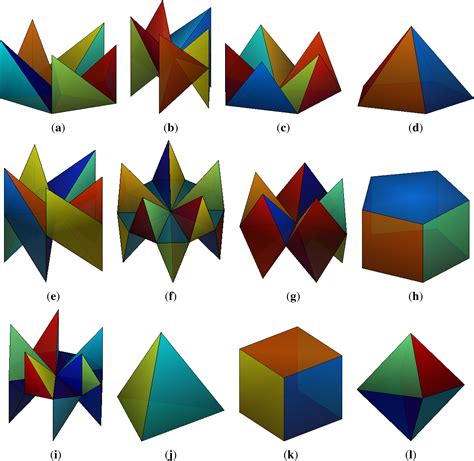
3D symmetry has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Symmetry is used in CAD software to create and manipulate 3D models. By applying symmetry operations, designers can quickly create complex shapes and patterns.
- 3D Printing: Symmetry is essential in 3D printing, where it is used to create complex shapes and structures. By applying symmetry operations, 3D printing software can optimize print jobs, reducing material waste and print time.
- Computer Graphics: Symmetry is used in computer graphics to create realistic models and animations. By applying symmetry operations, artists can create complex shapes and patterns, adding depth and realism to their work.
📝 Note: Symmetry is not limited to 3D objects. It can also be applied to 2D shapes and patterns, such as the symmetry of a snowflake or the symmetry of a repeating pattern.
Tools and Techniques for Creating 3D Symmetry

Creating 3D symmetry requires a range of tools and techniques, including:
- 3D Modeling Software: Software such as Blender, Maya, and 3ds Max offer a range of tools and features for creating and manipulating 3D models with symmetry.
- Symmetry Operations: Symmetry operations, such as reflection, rotation, and scaling, can be applied to 3D models to create symmetrical shapes and patterns.
- Scripting and Programming: Scripting languages, such as Python and JavaScript, can be used to automate symmetry operations and create complex shapes and patterns.
💻 Note: Creating 3D symmetry requires a good understanding of 3D modeling and mathematics. It is essential to have a solid foundation in these subjects before attempting to create complex symmetrical shapes and patterns.
Best Practices for Working with 3D Symmetry
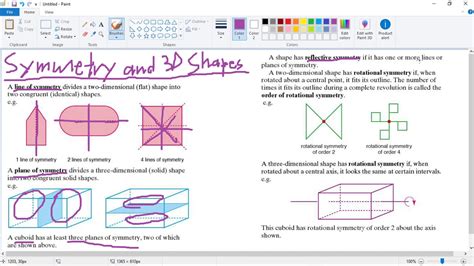
When working with 3D symmetry, it is essential to follow best practices, including:
- Plan Ahead: Before creating a 3D model, plan ahead and consider the symmetrical properties of the object.
- Use Reference Images: Use reference images to ensure that your 3D model is symmetrical and accurate.
- Test and Refine: Test and refine your 3D model regularly to ensure that it is symmetrical and meets your requirements.
By following these best practices, you can create complex 3D models with symmetry, adding depth and realism to your work.
In conclusion, 3D symmetry is a fundamental concept in various fields, including art, architecture, engineering, and mathematics. By understanding the types, importance, and applications of 3D symmetry, you can create complex shapes and patterns, adding depth and realism to your work. Remember to plan ahead, use reference images, and test and refine your 3D models regularly to ensure that they are symmetrical and accurate.
What is 3D symmetry?

+
3D symmetry refers to the quality of being unchanged under a particular transformation, such as rotation, reflection, or scaling.
What are the types of 3D symmetry?
+
There are several types of 3D symmetry, including reflection symmetry, rotational symmetry, helical symmetry, and screw symmetry.
What are the applications of 3D symmetry?

+
3D symmetry has numerous applications in various fields, including art, architecture, engineering, mathematics, computer-aided design, 3D printing, and computer graphics.