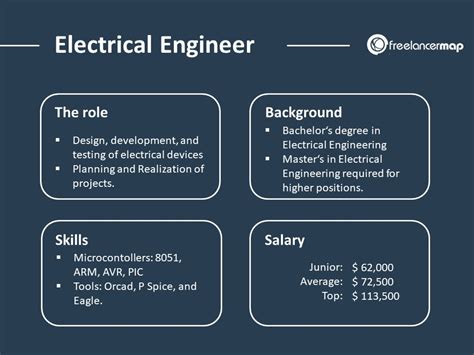
5 Key Roles of Electrical Engineers

The Multifaceted World of Electrical Engineers: 5 Key Roles
Electrical engineers play a crucial role in designing, developing, and maintaining electrical systems that power our homes, industries, and transportation systems. Their work has a significant impact on our daily lives, from the smartphones we use to the hospitals that rely on life-saving medical equipment. In this article, we’ll delve into the 5 key roles of electrical engineers and explore the various fields they work in.
Role 1: Design and Development

Electrical engineers are responsible for designing and developing new electrical systems, including electrical circuits, microprocessors, and embedded systems. They use computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulations to create and test their designs, ensuring they meet the required specifications and safety standards. This role requires a strong understanding of electrical theory, mathematics, and computer programming.
Some of the key activities involved in this role include:
- Designing and developing electrical systems for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare
- Creating prototypes and testing them to ensure they meet the required specifications
- Collaborating with cross-functional teams to integrate electrical systems with other systems, such as mechanical and software systems
📝 Note: Electrical engineers must stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and design tools to remain competitive in the field.
Role 2: Testing and Validation
Electrical engineers are responsible for testing and validating electrical systems to ensure they meet the required safety and performance standards. They use various testing tools and techniques, such as simulation software and testing equipment, to identify and debug errors in the system.
Some of the key activities involved in this role include:
- Conducting tests to ensure electrical systems meet safety standards and regulations
- Analyzing test data to identify errors and areas for improvement
- Collaborating with design teams to implement changes and improvements to the system
📊 Note: Electrical engineers must be meticulous and detail-oriented when testing and validating electrical systems to ensure they are safe and reliable.
Role 3: Installation and Commissioning

Electrical engineers are responsible for installing and commissioning electrical systems, ensuring they are properly connected and functioning as intended. This role requires a strong understanding of electrical theory and practical experience with electrical systems.
Some of the key activities involved in this role include:
- Installing electrical systems, including wiring, circuits, and electrical panels
- Commissioning electrical systems to ensure they are functioning correctly and efficiently
- Troubleshooting electrical systems to identify and resolve issues
🔧 Note: Electrical engineers must be skilled in the practical aspects of electrical engineering, including installation and commissioning of electrical systems.
Role 4: Maintenance and Repair

Electrical engineers are responsible for maintaining and repairing electrical systems to ensure they continue to function safely and efficiently. This role requires a strong understanding of electrical theory and practical experience with electrical systems.
Some of the key activities involved in this role include:
- Performing routine maintenance tasks, such as inspecting and replacing electrical components
- Troubleshooting electrical systems to identify and resolve issues
- Collaborating with other teams to ensure electrical systems are integrated with other systems, such as mechanical and software systems
🛠️ Note: Electrical engineers must be able to think critically and troubleshoot complex electrical systems to resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
Role 5: Research and Development

Electrical engineers are responsible for researching and developing new electrical technologies and systems, including renewable energy systems, energy storage systems, and smart grids. This role requires a strong understanding of electrical theory and a willingness to think creatively and outside the box.
Some of the key activities involved in this role include:
- Conducting research to identify new electrical technologies and systems
- Developing prototypes and testing them to ensure they meet the required specifications
- Collaborating with other teams to integrate new electrical systems with other systems, such as mechanical and software systems
💡 Note: Electrical engineers must be curious and open to new ideas and technologies to stay ahead of the curve in the field.
As we’ve seen, electrical engineers play a multifaceted role in designing, developing, testing, installing, maintaining, and researching electrical systems. Their work has a significant impact on our daily lives, and their expertise is essential in a wide range of industries. Whether you’re interested in designing electrical systems for the automotive industry or researching new renewable energy technologies, a career in electrical engineering can be rewarding and challenging.
In summary, the 5 key roles of electrical engineers are design and development, testing and validation, installation and commissioning, maintenance and repair, and research and development. Each role requires a strong understanding of electrical theory and practical experience with electrical systems. By understanding these roles, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the work of electrical engineers and the impact they have on our daily lives.
What is the role of an electrical engineer in the automotive industry?

+
Electrical engineers in the automotive industry design and develop electrical systems for vehicles, including electrical circuits, microprocessors, and embedded systems.
What skills do electrical engineers need to have to be successful?

+
Electrical engineers need to have a strong understanding of electrical theory, mathematics, and computer programming, as well as practical experience with electrical systems.
What is the future outlook for electrical engineers?
+
The demand for electrical engineers is expected to grow in the coming years, driven by the increasing need for electrical systems in industries such as renewable energy, healthcare, and transportation.



