Mastering Remote Center Motion with STL Files
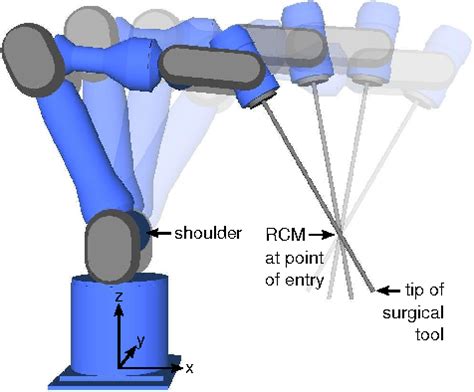
Understanding Remote Center Motion (RCM)
Remote Center Motion (RCM) is a critical concept in the field of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and 3D printing. It refers to the ability of a 3D printer or CNC machine to move its toolhead or end effector in a way that maintains a fixed point or axis, relative to the workpiece or object being fabricated. This fixed point is often referred to as the “remote center” or “kinematic center.”
In the context of STL files, RCM is essential for achieving accurate and precise 3D printing results. STL (STereoLithography) files are widely used in 3D printing and CAD software to represent 3D models. They contain information about the surface geometry of the model, which is used to generate toolpaths for 3D printing or CNC machining.
Importance of RCM in STL Files
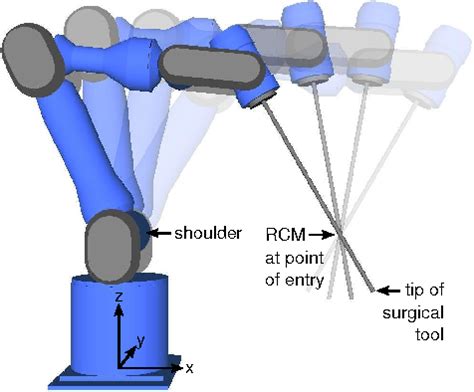
RCM is crucial in STL files because it enables the 3D printer or CNC machine to accurately follow the contours of the 3D model. Without RCM, the toolhead or end effector may not maintain a consistent distance from the workpiece, resulting in inaccurate or distorted prints.
In particular, RCM is essential for:
- Accurate contouring: RCM ensures that the toolhead or end effector follows the contours of the 3D model accurately, resulting in precise and smooth curves.
- Reduced vibration: By maintaining a fixed point or axis, RCM reduces vibration and oscillation of the toolhead or end effector, resulting in improved print quality and reduced wear on the machine.
- Improved surface finish: RCM enables the 3D printer or CNC machine to maintain a consistent surface finish, resulting in a smoother and more even finish.
Mastering RCM with STL Files

To master RCM with STL files, follow these steps:
- Use a 3D modeling software: Create your 3D model using a software that supports STL files, such as Blender, Fusion 360, or Tinkercad.
- Optimize your STL file: Ensure that your STL file is optimized for 3D printing by reducing the polygon count, removing unnecessary features, and smoothing out curves.
- Use a 3D printing slicer: Use a 3D printing slicer software, such as Cura or Slic3r, to generate toolpaths from your STL file. These software programs can help you optimize RCM by adjusting parameters such as infill density, layer height, and toolhead speed.
- Adjust RCM parameters: Adjust RCM parameters, such as the kinematic center or remote center, to optimize the movement of the toolhead or end effector. This may involve adjusting the X, Y, and Z coordinates of the kinematic center or remote center.
- Simulate and visualize: Simulate and visualize your 3D print or CNC machining process to ensure that RCM is working correctly. This can help you identify any issues or errors before starting the actual fabrication process.
Tips and Tricks for Mastering RCM
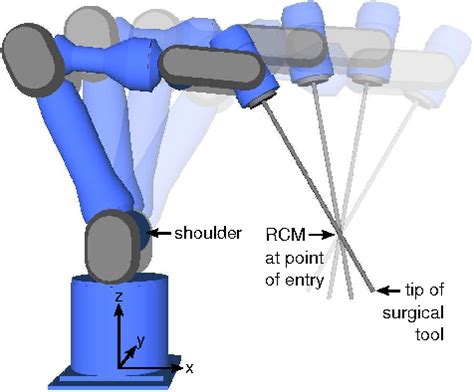
Here are some additional tips and tricks for mastering RCM with STL files:
- Use a consistent unit system: Ensure that your 3D modeling software, 3D printing slicer, and STL file use a consistent unit system (e.g., millimeters or inches).
- Avoid excessive complexity: Avoid creating 3D models with excessive complexity, as this can make it difficult to optimize RCM.
- Use a kinematic center or remote center: Use a kinematic center or remote center to define the fixed point or axis of the toolhead or end effector.
- Experiment with different RCM parameters: Experiment with different RCM parameters, such as the kinematic center or remote center, to optimize the movement of the toolhead or end effector.
| RCM Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Kinematic Center | Defines the fixed point or axis of the toolhead or end effector |
| Remote Center | Defines the fixed point or axis of the toolhead or end effector, relative to the workpiece or object being fabricated |
| Toolhead Speed | Controls the speed of the toolhead or end effector |
| Infill Density | Controls the density of the infill material |

💡 Note: Mastering RCM with STL files requires a deep understanding of 3D modeling, 3D printing, and CNC machining. It is essential to experiment with different RCM parameters and techniques to optimize the movement of the toolhead or end effector.
By following these steps and tips, you can master RCM with STL files and achieve accurate and precise 3D printing results.
What is Remote Center Motion (RCM)?
+
Remote Center Motion (RCM) is a critical concept in the field of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and 3D printing. It refers to the ability of a 3D printer or CNC machine to move its toolhead or end effector in a way that maintains a fixed point or axis, relative to the workpiece or object being fabricated.
Why is RCM important in STL files?

+
RCM is crucial in STL files because it enables the 3D printer or CNC machine to accurately follow the contours of the 3D model. Without RCM, the toolhead or end effector may not maintain a consistent distance from the workpiece, resulting in inaccurate or distorted prints.
How can I master RCM with STL files?

+
To master RCM with STL files, use a 3D modeling software, optimize your STL file, use a 3D printing slicer, adjust RCM parameters, and simulate and visualize your 3D print or CNC machining process.



